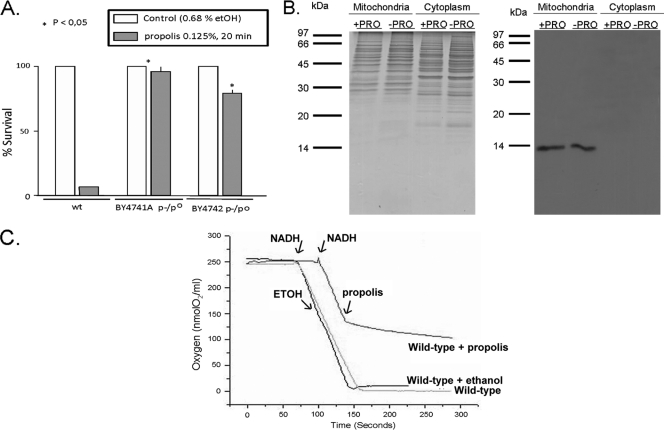
Fig. 8.
Petite mutants are more tolerant to propolis. (A) Viability of 16-h yeast wild-type and petite mutant strains to 0.125% propolis (*, P < 0.05) was determined by plating appropriated cell concentrations and counting the number of colonies. The results are the means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. (B) Exposure of yeast petite mutant cells to propolis does not induce cytochrome c release into the cytoplasm. Yeast cells were grown for 16 h at 30°C and left untreated or exposed to 0.125% propolis for 10 min at 30°C. The cells were harvested and fractionated (mitochondria and cytoplasm) as described in the Materials and Methods section, and proteins were run on a polyacrylamide gel. At left is a Coomassie-stained gel with the same amount of proteins that were transferred to a nitrocellulose filter (right panel). This membrane was probed with the antibody rabbit anti-cytochrome c. (C) NADH oxidase activity in wild-type yeast in the presence of propolis. Mitochondria (100 μg of protein) of the wild-type W303 strain were assayed for NADH-oxidase with a Clark electrode as described in the Materials and Methods section. Arrows indicate the addition of propolis (final concentration of 0.125%) or the identical volume of ethanol and KCN. These are representative traces of one experiment, which were reproduced with mitochondria isolated on three different days.