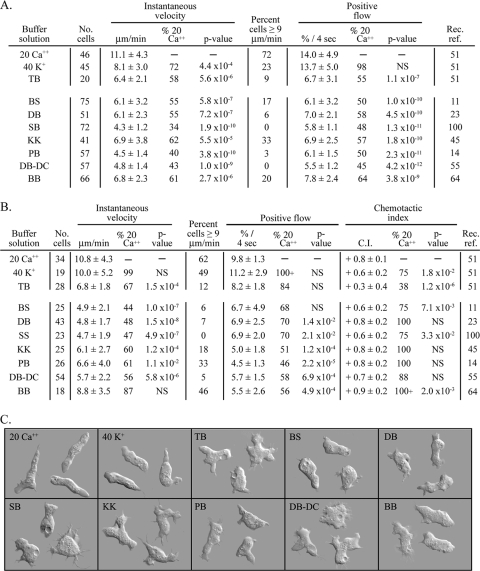
Fig. 1.
Motile behavior of Dictyostelium discoideum, analyzed in buffers commonly used by researchers studying motility and chemotaxis. The composition of the solutions is provided in Table 1. Cell motility and cell polarization were maximal in solutions containing facilitating concentrations of Ca2+ and K+ but not in the majority of commonly used buffers, which do not contain facilitating concentrations of either cation. This was true in both the absence and the presence of a cAMP gradient. Chemotactic orientation in a cAMP gradient, however, was equally efficient in all tested buffers. (A) Motility parameters in test solutions in the absence of cAMP. (B) Motility and chemotaxis parameters in a cAMP spatial gradient. (C) Differential interference contrast microscopy images of cells crawling in the buffer solutions indicated in the upper left corner of each panel in the absence of cAMP. Parameters in panels A and B are defined in Materials and Methods. Values in panels A and B are the means ± standard deviations for the population. No. cells, number of cells analyzed; Rec. ref., Recent reference for buffer; see Table 1 for abbreviations. The P value for parameters in each test solution versus 20 mM Ca2+ were determined by the Student t test; NS, not significant for P values of >5.0 × 10−2.