Fig. 3.
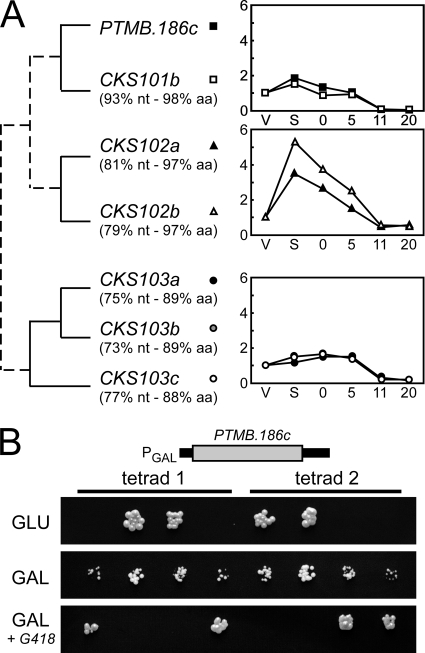
PTMB.186c encodes a homolog of cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit Cks1p. (A) CKS-like genes in P. tetraurelia and their transcription profiles during autogamy. Paralogs of gene PTMB.186c (CKS101a) are CKS101b (PTETG800015001), CKS102a (GSPATG00005766001), CKS102b (GSPATG00007882001), CKS103a (GSPATG00004184001), CKS103b (GSPATG00010146001), and CKS103c (GSPATG00024666001). The percentages of nucleotide sequence identity (nt) and amino acid identity (aa) of the predicted gene product relative to PTMB.186c are indicated below each paralog. WGD paralogs are linked by solid lines; other evolutionary relationships are indicated by dotted lines. Transcription profiles were determined following hybridization of whole genome microarrays with cDNAs from two independent autogamy time course experiments performed with strain 51 (see the supplemental material). For each gene, mean hybridization signals obtained at each time point throughout autogamy were normalized relative to the value calculated for vegetative cells. (B) Complementation of a null cks1 mutation by the product of PTMB.186c in S. cerevisiae. A diploid S. cerevisiae strain carrying both a wild-type CKS1 and a null cks1::kanMX4 allele was made by inserting a G418 resistance cassette in the CKS1 coding sequence. It was transformed with a plasmid carrying the Paramecium PTMB.186c gene under the control of the S. cerevisiae GAL1 promoter, which is strongly induced by galactose (GAL) and repressed by glucose (GLU). Therefore, growing cells on galactose or glucose controls the expression of the P. tetraurelia CKS1 homolog. The transformed diploid strain was sporulated in order to segregate each allele into haploid spores. From each tetrad, only spores carrying a wild-type CKS1 gene were viable under repressive conditions (GLU). Under inducing conditions (GAL), normal-sized colonies were obtained from spores harboring a wild-type endogenous CKS1 allele, and smaller-sized colonies were obtained if a null background was complemented by exogenous PTMB.186c. In the latter case, the presence of the cks1::kanMX4 allele was confirmed by spotting on YP GAL + G418 medium, selective for the antibiotic resistance phenotype.