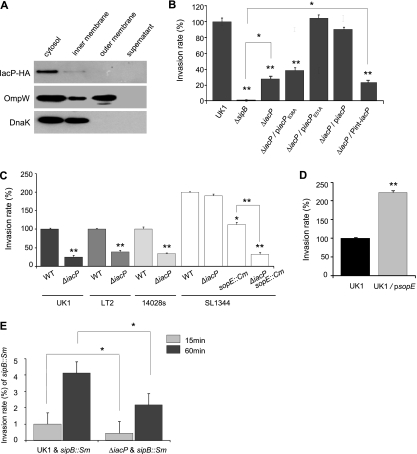
FIG. 1.
IacP contributes to Salmonella serovar Typhimurium invasion into nonphagocytic cells. (A) Salmonella serovar Typhimurium bacteria grown under SPI-1-inducing conditions were fractionated on a sucrose gradient. HA-tagged IacP was detected in the cytoplasmic fraction. As a control for the membrane and cytoplasmic proteins, the blot was reprobed with antibodies against OmpW and DnaK. (B to E) To determine the invasion rate, bacterial strains were allowed to infect an INT-407 cell for 15 min or 60 min, after which a gentamicin protection assay was conducted. The intracellular bacteria were enumerated by the plating of serial dilutions, and the percent bacterial invasion rate was calculated in comparison to that of the wild type (WT), which was set as 100% (in the case of strain SL1344, the invasion rate of UK1 was set as 100%). All experiments were performed on separate days at least three times. Bars correspond to the means ± standard deviations (SD). *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001 (compared with invasion by the respective wild-type or control strain, determined by a Student's t test).