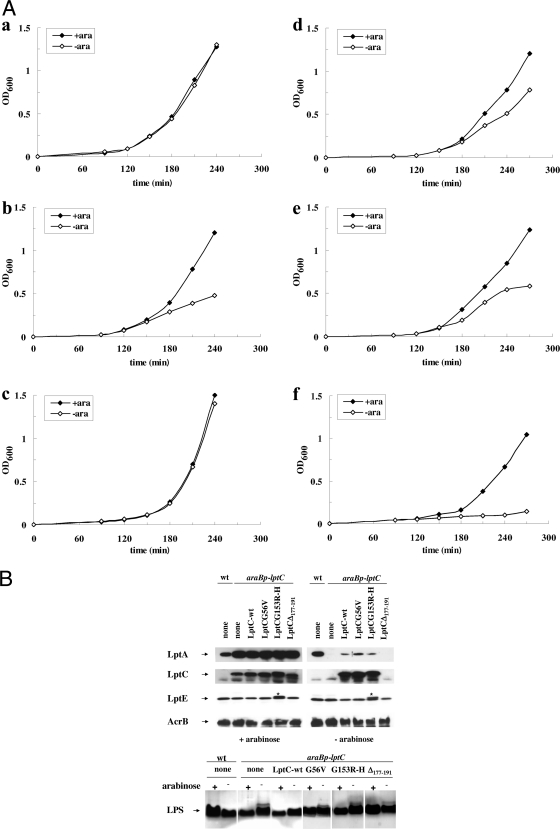
FIG. 5.
Effect of lptC mutations on Lpt proteins complex and LPS transport. (A) Growth curves of AM604 (wt; a), FL905 (araBp-lptC; b) strains and FL905 carrying plasmids expressing LptC (c), LptCG56V (d), LptCG153R-H (e), and LptCΔ177-191 (f). Cells growing exponentially in LD containing arabinose were harvested, washed, and subcultured in arabinose-supplemented (⧫) or arabinose-free (⋄) medium. Growth was monitored by measuring the OD600. Samples for protein and LPS analyses were taken from cells grown in the presence (+ara) or absence (−ara) of arabinose at 240 (wt, FL905, and FL905/pGS103) or 270 min (FL905/pGS103G56V, FL905/pGS108G153R, and FL905/pGS103Δ177-191) after the shift into fresh medium. (B) Steady-state levels of LptA, LptC, and LptE and LPS profile. Protein samples were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-LptA, anti-LptC, anti-LptE, and anti-AcrB (as a loading control) antibodies. Anti-LptE antibodies cross-react with LptC-H His tag (*). Total LPS was extracted from mutant cells grown in the same conditions and at the same time points of protein analysis. LPS extracted from cultures with a total OD600 of 2 were separated by 18% Tricine-SDS-PAGE and silver stained. Equal amounts of cells, based on the OD measurement (0.2 OD600 units for protein analysis, 0.4 for LPS analysis), were loaded into each lane.