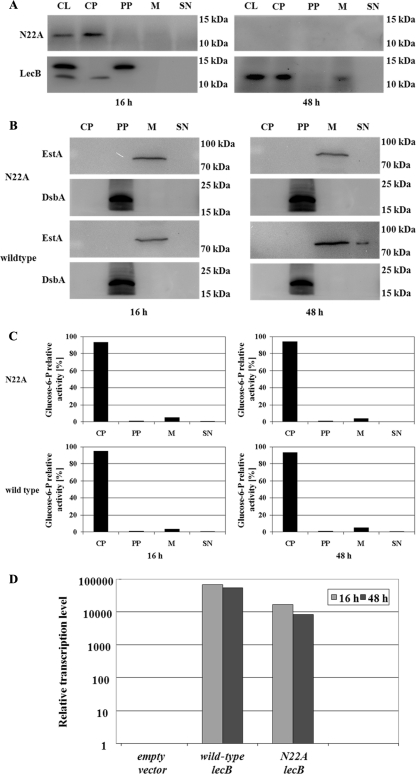
FIG. 4.
Secretion defect of the nonglycosylated LecB variant in the LecB-deficient strain P. aeruginosa PATI2, and controls to validate the cellular fractionation procedure. The asparagine residue (N) of the putative N glycosylation site (NXS/T) was replaced by alanine (A) by site-directed mutagenesis. The variant gene was cloned into pBBR1MCS under transcriptional control of the lac promoter and expressed in the LecB-deficient background of strain P. aeruginosa PATI2. (A) Subcellular localization of wild-type and mutant LecB (N22A mutant) in P. aeruginosa biofilm cells. Localization was determined by isolation of cellular compartments after growth periods of 16 and 48 h at 37°C on NB agar plates and subsequent Western immunoblotting using a LecB-specific antiserum. (B and C) Validation of cellular fractionation procedure was performed by immunoblotting using an antiserum raised against the periplasmic protein DsbA and the outer membrane protein EstA (B) and by distribution of the activity of the cytoplasmic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (C). The percentages of total enzyme activities present in cytoplasm, periplasm, membrane, and culture supernatant are given. (D) Relative transcription levels of the lecB variant gene lecB(N22A) in P. aeruginosa cells. RNA was isolated from the lecB-deficient P. aeruginosa strain PATI2 containing the plasmid pBBN22A [lecB(N22A)] encoding mutant LecB after growth periods of 16 and 48 h. As a positive control, mRNA isolated from the lecB-deficient P. aeruginosa strain PATI2 containing the lecB expression plasmid pBBC2 (wild-type lecB) was used. Detection of lecB and lecB(N22A) was achieved by using a specific TaqMan gene expression assay (Applied Biosystems, Switzerland). The transcription levels of the genes were normalized to that of the housekeeping gene rpoD and related to the lecB transcription level of the lecB-deficient strain PATI2 containing the empty vector pBBR1MCS. All values for the transcription levels investigated in this study represent means of at least three measurements; standard deviations were less than 5%. CL, cell lysate; CP, cytoplasm; PP, periplasm; M, membrane; SN, culture supernatant.