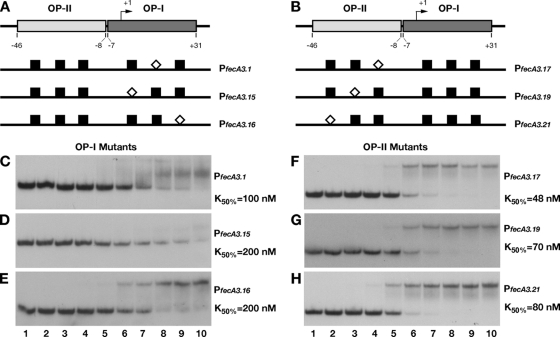
FIG. 3.
DNA binding assays of mutant promoters. The introduction of a SmaI site in place of the bases protected by hydroxyl radical cuts on both operators strongly affected the affinity of HpNikR for the whole promoter. A schematic representation of base substitutions within OP-I (A) and OP-II (B) is shown, with the white diamonds indicating the position of SmaI with respect to the wild-type sites (black boxes). Six mutant operator probes were generated (PfecA3.1 [C], PfecA3.15 [D], PfecA3.16 [E], PfecA3.17 [F], PfecA3.19 [G], and PfecA3.21 [H]) and analyzed by DNA retardation assay. HpNikR was added at the following concentrations: 0 nM (no protein) (lanes 1), 0.34 nM (lanes 2), 3.4 nM (lanes 3), 9.8 nM (lanes 4), 34 nM (lanes 5), 68.6 nM (lanes 6), 137.2 nM (lanes 7), 274.4 nM (lanes 8), 343 nM (lanes 9), and 686 nM (lanes 10). The K50 was calculated as described for the wild-type construct (see legend to Fig. 2); in all cases, the standard deviation was less than 10% of the K50 value reported on the right site of each panel (C to H).