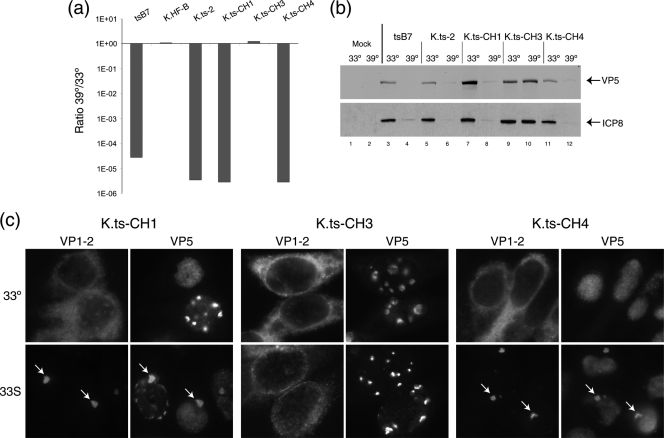
FIG. 8.
Identification of a single residue change responsible for the ts phenotype of tsB7 and K.ts-2. (a) tsB7, K.ts-2 (containing the four changes present in tsB7 UL36), and variants with subsets of these changes were analyzed for plaque formation in Vero cells at 39°C versus 33°C. K.ts-CH1 and K.ts-CH4 exhibited a reduction of approximately 5 log units in plaque formation, while K.ts-CH3 (containing three of the four substitutions but wt at position 1453) exhibited no defect in plaque formation. (b) Temperature sensitivity of gene expression. Vero cells were infected (MOI, 5) with viruses as indicated at 33°C or 39°C, and extracts were collected at 24 h postinfection and analyzed for the accumulation of viral proteins VP5 and ICP8. Actin levels were measured as a loading control. (c) Altered localization of ts VP1-2 after temperature shift. Hep2 cells were infected with the indicated viruses at 33°C and at 10 h postinfection either maintained at 33°C or shifted up to 39°C. Cells were fixed at 16 h postinfection and the localization of VP1-2 and VP5 analyzed. At 39°C, pronounced relocalization of VP1-2, colocalizing with VP5 in a single juxtanuclear aggregate, is evident (arrows) for K.ts-CH1 and for K.ts-CH4, which contain, respectively, 1061D → G plus 1453Y → H or just 1453Y → H. No alteration in VP1-2 localization was observed for K.ts-CH3, which contains three tsB7 substitutions, but the wt residue at position 1453.