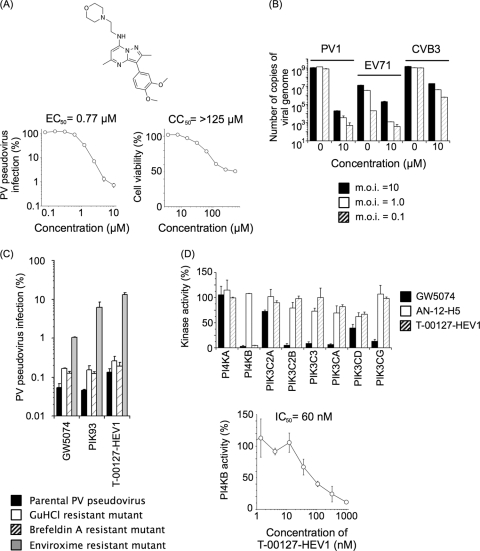
FIG. 1.
Characterization of T-00127-HEV1 and inhibitory effects on PI kinases. (A) Characterization of T-00127-HEV1. Upper panel, structure of T-00127-HEV1. Lower panels, inhibitory effect of T-00127-HEV1 on PV pseudovirus (left panel) and viability of RD cells (right panel). PV pseudovirus infection in the absence of compounds was taken as 100%. (B) Inhibitory effect of T-00127-HEV1 on enterovirus infection. RD cells were infected with PV1(Mahoney), EV71(Nagoya), or CVB3(Nancy) at MOI of 10, 1.0, and 0.1 in the absence of T-00127-HEV1 and then were treated with 0 or 10 μM T-00127-HEV1 from 1 h p.i. The total number of copies of viral genomes in the cells at 16 h p.i. is shown. (C) Specificity of mutations causing resistance to antienterovirus compounds. RD cells were infected with PV pseudovirus mutants that have mutations causing resistance to GuHCl (U4614A), brefeldin A (G4361A plus C5190U), and enviroxime (G5318A) in the presence of antienterovirus compounds GW5074 (25 μM), PIK93 (1.3 μM), and T-00127-HEV1 (4.0 μM). PV pseudovirus infection in the absence of compounds was taken as 100%. (D) Inhibitory effects of enviroxime-like compounds on in vitro activities of PI kinases. Upper panel, in vitro activities of PI kinases were analyzed in the presence of enviroxime-like compounds (GW5074, AN-12-H5, and T-00127-HEV1 at a concentration of 10 μM) with an ATP concentration of 10 μM. Lower panel, inhibitory effect of T-00127-HEV1 on the in vitro PI4KB activity measured with an ATP concentration of 10 μM.