FIG. 3.
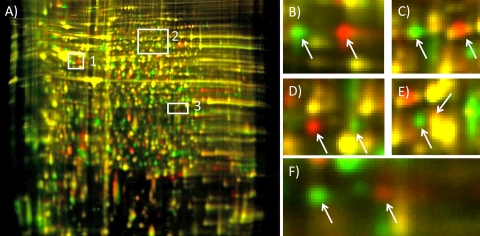
Numerous proteins associated with the CYDV-RPV transmission-competent phenotype in the competent parent and competent F2 genotypes had an isoform inherited from the maternal lineage that differed in pI. (A) pH 3 to 10, nonlinear, 24-cm DIGE gel of protein extracts from competent and refractive genotypes. Boxes highlight areas of the gel containing pI isoforms segregating in the Schizaphis graminum populations that differ in CYDV-RPV vectoring capacity. Proteins from transmission-competent genotypes are labeled with Cy3 (green), and proteins from the refractive genotype are labeled with Cy5 (red). (B) From the area in box 1, pI isoforms of troponin-T. (C) From the area in box 2, pI isoforms of replication protein A 70-kDa subunit. (D) From the area in box 2, pI isoforms of CoA ligase. (E) From the area in box 2, pI isoforms of electron-transferring flavoprotein dehydrogenase. (F) From the area in box 3, pI isoforms of GAPDH. In some instances (E), one isoform had a pI and molecular weight similar to those of another protein and could not be resolved from that comigrating protein, which was not differentially expressed (yellow signal resulting from signals in both Cy3 and Cy5 channels). The gel was visualized using a Typhoon variable-mode imager (GE Healthcare) according to the manufacturer's instructions on imaging cyanine dyes.