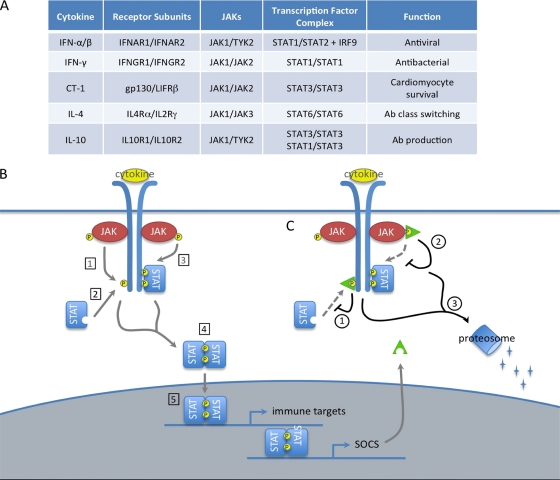
FIG. 2.
SOCS proteins negatively regulate the JAK/STAT pathway. (A) Composition of selected JAK/STAT pathways. (B) Function of JAK/STAT pathway. Cytokine stimulation of cell surface receptors activates receptor-associated JAK proteins by phosphorylation (P). Activated JAKs phosphorylate receptor cytoplasmic domains (1), which leads to the recruitment of cytoplasmic STAT proteins (2). Recruited STATs are activated by JAK phosphorylation (3), allowing them to dimerize (4) and enter the nucleus as a transcription factor complex to induce the expression of target genes. Gene targets often include both immune effectors and SOCS proteins. (C) SOCS proteins. SOCS proteins negatively regulate this pathway by binding specific substrates within the JAK/STAT receptor complex and terminating pathway activation in one of the following ways: competition with recruited STAT proteins for shared phosphotyrosine residues (1), kinase inhibitory region (KIR)-mediated inhibition of JAK activity (2), or SOCS box-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of bound receptor components (3).