FIG. 3.
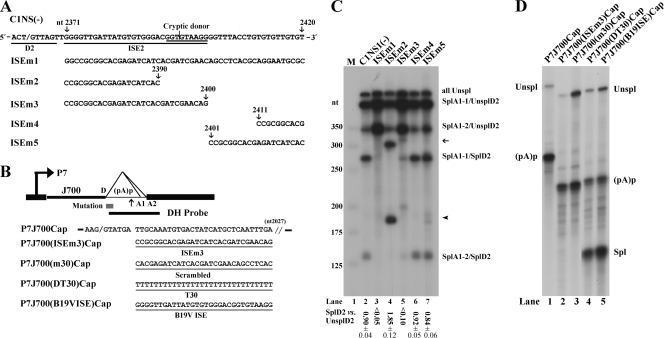
Intronic splicing enhancer (ISE) immediately 3′ of the D2 donor site. (A) The D2 site and its neighboring G/GU-rich sequence in the B19V genome are depicted, with the locations of five mutations in this region indicated (arrows plus nucleotide number). The D2 site, identified cryptic donor site, and identified ISE2 sequence are underlined, and the mutant constructs used for RNase protection assays in panel B are shown below. (B) The test construct P7J700Cap (previously described in reference 15) is diagramed with the location of the DH probe indicated (16). The AAV5 donor (D) site and the sequence to nt 2027 of the AAV5 genome (3) are shown. P7J700Cap and its derivatives, P7J700(ISEm3)Cap, P7J700(m30)Cap, P7J700(DT30)Cap, and P7J700(B19VISE)Cap, were constructed by mutating the sequence between nt 2097 and 2027 as shown. (C) RNase protection assays showing the functionality of the ISE2 and the cryptic donor. RNase protection assays of RNAs generated in COS-7 cells following transfection of the C1NS1(−) parent and of its mutant forms are shown with identities of the bands indicated to the right. A representative protection assay from at least three independent experiments is shown. The ratio of SplD2 to UnsplD2 is shown for each protection assay; some are given as averages and standard deviations. SplD2 includes signals from bands of SplA1-1/SplD2 and SplA1-2/SplD2, and UnsplD2 includes signals from bands of SplA1-1/UnsplD2, SplA1-2/UnsplD2, and allUnspl. The arrow and arrowhead show RNAs spliced from the A1-1 and A1-2 sites to the cryptic donor, respectively. (D) RNase protection assays showing that the B19V ISE2 promotes AAV5 RNA when lengths of the 5′ exon increase. For these experiments, total RNA isolated from plasmid-transfected COS-7 cells was subjected to RNase protection assays using probe DH (shown in panel B), as previously described (15). Unspl, RNA unspliced at the AAV5 donor site; Spl, RNA spliced at the AAV5 donor site; and (pA)p, RNA polyadenylated at the AAV5 (pA)p site.