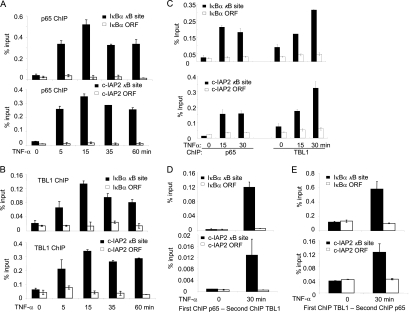
FIG. 3.
TNF-α induces the recruitment of TBL1 and p65 to the NF-κB target gene promoter. (A) TNF-α-induced p65 binding to the IκBα and c-IAP2 promoters in M4e cells. M4e cells were treated with TNF-α for different times as indicated. ChIP assays were performed with a ChIP assay kit from Upstate Biotechnology with anti-p65 antibodies. Values are means ± standard deviations for triplicate samples from a representative experiment. (B) TNF-α-induced TBL1 binding to the IκBα and c-IAP2 promoters in M4e cells. M4e cells were treated with TNF-α for different time points as indicated. ChIP assays were performed using anti-TBL1 antibodies. Values are means ± standard deviations for triplicate samples from a representative experiment. (C) TNF-α induces the recruitment of TBL1 and p65 to the NF-κB target gene promoter in HT1080 cells. TNF-α induced TBL1 and p65 binding to the IκBα and c-IAP2 promoters in HT1080 cells. Cells were treated with TNF-α for 0, 15, and 30 min. ChIP assays were performed with a ChIP assay kit from Upstate Biotechnology with anti-p65 and anti-TBL1 antibodies. Values are means ± standard deviations for triplicate samples from a representative experiment. (D) p65 and TBL1 cooccupy the NF-κB target gene promoter, as determined in a re-ChIP assay. M4e cells were treated with TNF-α for 0 and 30 min. The chromatin complexes were first precipitated with anti-p65 antibodies and then subjected to re-ChIP with anti-TBL1 antibodies. Sequentially enriched genomic DNA was amplified by real-time PCR using specific IκB-α and c-IAP2 primer sets. (E) Reverse re-ChIP assays confirming cooccupancy of p65 and TBL1 on the NF-κB target gene promoter. The chromatin complexes were first immunoprecipitated with anti-TBL1 antibodies and then with anti-p65 antibodies.