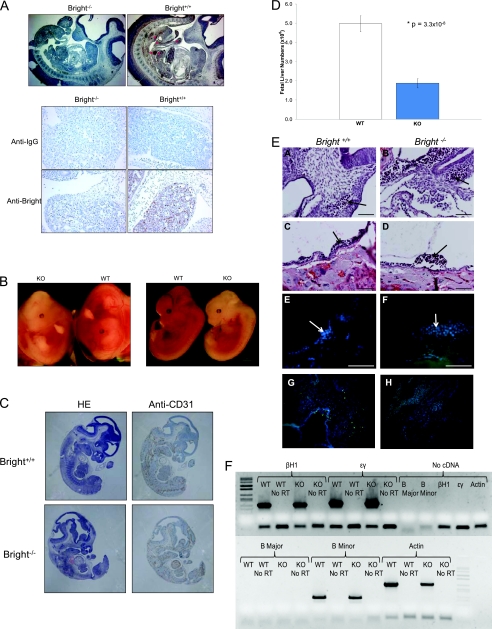
FIG. 2.
Analysis of Bright null embryos. (A) Bright expression in E12.5 embryos is restricted primarily to the fetal liver (arrows). Sections from a Bright knockout embryo and a control littermate embryo were stained with anti-Bright antibody (top and bottom) or an isotype control (anti-IgG; middle). Red arrows indicate punctate areas of intense staining within the intestine. No morphological pathogenesis was observed elsewhere. Magnification: upper panel, ×25; lower panel, ×200. (B) Bright−/− embryos exhibit extreme pallor at E12.5. A Bright knockout embryo has significantly fewer circulating erythrocytes than its littermate control in both the yolk sac (left panel) and the embryo (right panel). (C) Bright−/− embryos show normal expression of the endothelial cell marker CD31, suggesting that vascular development is normal. Sections from E12.5 Bright−/− and control Bright+/+ embryos were stained with hematoxylin (HE, left) and anti-CD31 (right). (D) E12.5 Bright−/− fetal livers are hypocellular. Whole E12.5 fetal livers from 33 wild-type (WT) and 25 Bright null (KO) embryos were isolated and placed in a single-cell suspension, and total cell numbers were counted. Student's t test shows significantly lower numbers of cells in the Bright null livers. (E) E9.5 Bright−/− erythrocytes are normal. Wild-type and Bright−/− littermate embryos (A and B) and yolk sacs (C and D) contain blood vessels with comparable numbers of circulating erythrocytes. Erythrocytes found in wild-type and Bright−/− embryonic vessels (E and F) and yolk sac vessels (G and H) are nonapoptotic, as evidenced by a lack of TUNEL staining (blue, DAPI; green, TUNEL). Blood vessels are outlined for identification. Scale bars, 100 μm. (F) The reduced number of Ter119+ null fetal liver reticulocytes at E12.5 contain levels of embryonic (ɛY and βH1) and fetal/adult (βmaj [B Major] and βmin [B Minor]) globins comparable to those of the controls. RT-PCR and cell fractionations were performed as detailed in Materials and Methods.