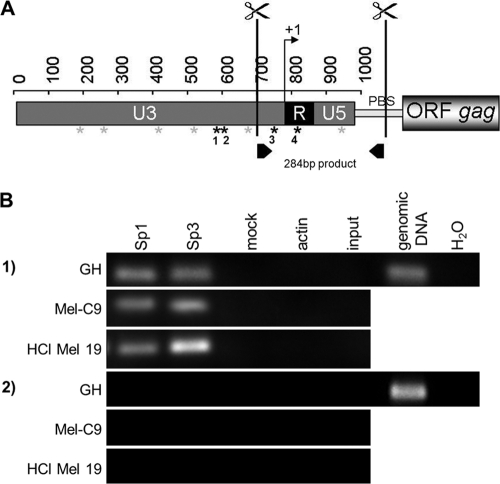
FIG. 6.
Sp1 and Sp3 bind to HERV-K LTRs in vivo. (A) ChIP assays were performed, with cutting of proviral HERV-K LTRs at the indicated sites. Putative binding sites for Sp1/Sp3 are depicted by asterisks; black asterisks indicate sequence differences between LTRpck30 and LTR21 in four Sp1/Sp3 binding motifs. (B) Immunoprecipitation was performed with antibodies directed against Sp1, Sp3, or actin. Specific PCR primers excluding amplification of products from solitary LTRs were used to analyze the precipitates (see panel A; PBS denotes the primer binding site), as well as env-specific primers. PCRs on digested and cross-linked fragments before the immunoprecipitation step (input) and on mock IPs served as negative controls, as well as PCR without a template (H2O). Genomic DNA from GH cells was amplified as a positive control. ChIP with anti-Sp1 and anti-Sp3 antibodies yielded PCR amplicons with LTR-specific primers but not env-specific primers.