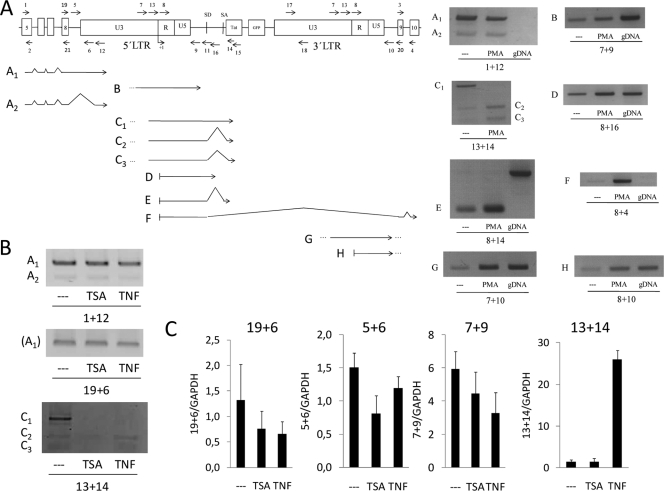
FIG. 2.
PCR-mediated identification of transcripts generated at latent HIV integration sites. (A) RNA extracted from J-Lat E27 cells treated or not with PMA (10 nM) for 16 h was used to generate cDNA by reverse transcription with random hexamers. Several oligonucleotide combinations were used on PCR amplification experiments to detect the appearance of different transcripts, shown in the figure below a schematic representation (out of scale) of the HIV minigenome at the UBXD8 intron 8. The HIV integration divides intron 8 into two pieces of 404 bp (upstream) and 1,846 bp (downstream). The positions of PCR primers used are indicated by arrows. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products illustrating each of the cDNA species is shown. When required, DNA sequencing of PCR products was applied to identify the exact nature of a cDNA fragment (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). PCR amplification from genomic DNA was performed as a product size control where indicated. (B and C) J-Lat E27 cells were treated or not with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) or TSA (400 nM) for 16 h, and transcripts were characterized by RT-PCR with the oligonucleotide pairs indicated, by conventional PCR (B) or real-time PCR (C). Primer pairs 19 plus 6 and 5 plus 6 detected the transcript named A1, primer pair 7 plus 9 measured transcript B, and primer pair 13 plus 14 measured transcripts C.