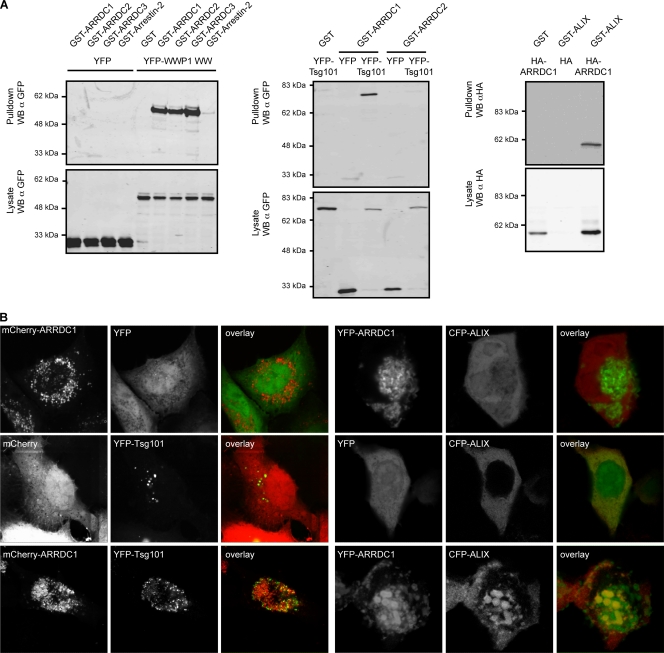
FIG. 2.
(A) Coprecipitation assays showing interactions of ARRDC1, -2, and -3 with WWP1 (WW domains) (left), of ARRDC1 and -2 with Tsg101 (middle), and of ARRDC1 with ALIX (right). Proteins fused to GST, HA, or YFP were transiently expressed in 293T cells as indicated, and GST-tagged proteins were precipitated using glutathione-Sepharose beads. Samples were analyzed for coprecipitated binding partners by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting (WB). Figures shown are representative of at least two independent experiments. α, anti. (B) Colocalization of ALIX and Tsg101 with ARRD1. Proteins fused to mCherry, YFP, or CFP as indicated were transiently expressed in 293T cells, and fixed cells were analyzed for protein colocalization by confocal microscopy. Pictures shown are representative of at least two independent experiments. Colocalization of coexpressed proteins was quantified by calculating the Pearson's correlation coefficient using Image J public domain image processing software (plug-in). This analysis yielded the following results: mCherry-ARRDC1/YFP, −0.07 ± 0.18 (n = 7); mCherry/YFP-Tsg101, 0.10 ± 0.07 (n = 8); mCherry-ARRDC1/YFP-Tsg101, 0.7 ± 0.18 (n = 11); YFP-ARRDC1/CFP, −0.26 ± 0.16(n = 12); YFP/CFP-ALIX, 0.55 ± 0.11 (n = 7); YFP-ARRDC1/CFP-ALIX, 0.69 ± 0.11 (n = 9). Data are represented as average value ± standard deviation. n, number of analyzed cells.