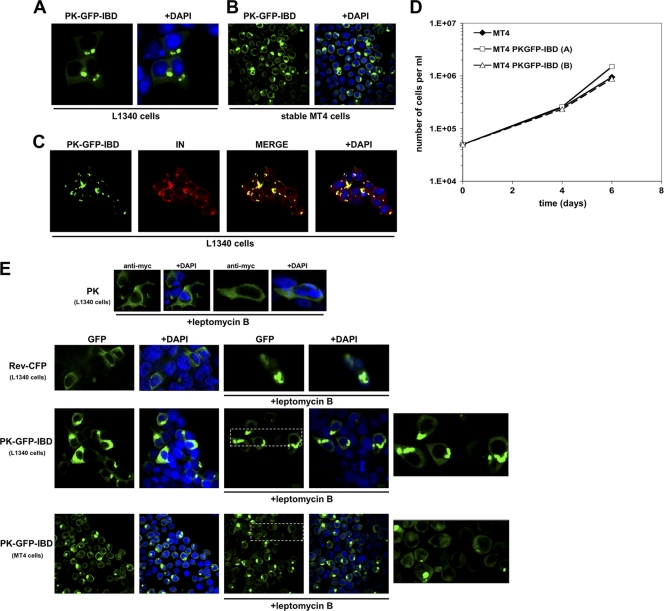
FIG. 8.
Characterization of a cytoplasmically restricted DI protein. (A) LEDGF-deficient 293T cells (L1340 cells [31]) were transfected with PK-GFP-IBD. Cells were fixed, and stained with DAPI at 48 h after transfection, and imaged with a confocal microscope. (B) MT4 cells stably expressing PK-GFP-IBD were centrifuged onto slides and imaged as described in Materials and Methods. (C) PK-GFP-IBD and Myc-epitope-tagged IN expression plasmids were transiently transfected into L1340 cells. Cells were fixed 48 h later and stained with anti-Myc. (D) Proliferative properties of MT4 cell lines derived by lentiviral vector transduction. (The “A” cell line is shown in the photomicrographs of this figure). (E) PK-GFP-IBD does not shuttle. PK-, Rev-CFP-, or PK-GFP-IBD-transfected L1340 cells or a stable CD4+ T cell line (MT4) expressing PK-GFP-IBD were each treated with leptomycin B to assess shuttling via the CRM1 pathway. The positive control in the experiment was Rev-CFP, which was imaged in the green channel to distinguish it from DAPI. In the presence of leptomycin B, Rev-CFP becomes completely nucleolar. In contrast, pyruvate kinase (PK; detected with an Alexa Green-conjugated antibody to the N-terminal Myc epitope tag) and PK-GFP-IBD remain completely cytoplasmic under the same conditions. The areas marked by dashed line boxes are enlarged at right.