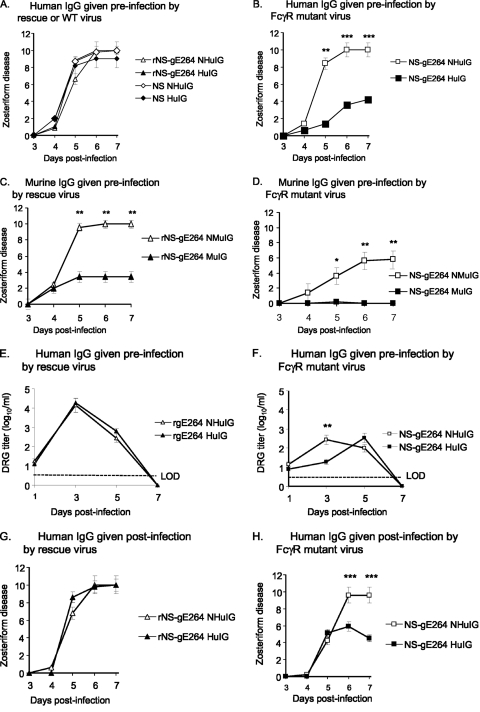
FIG. 7.
The HSV-1 FcγR blocks IgG Fc-mediated activities in the murine flank model. (A and B) Mice were passively immunized with 200 μg of human IgG antibody to HSV (human immune globulin [HuIG]) or nonimmune human IgG (NHuIG), and 20 h later they were flank inoculated with 5 × 105 PFU of rNS-gE264 or NS (A) or 5 × 105 PFU NS-gE264 (B). No differences were detected for the results shown in panel A, while zosteriform disease was significantly lower in the HuIG group on days 5 to 7 in the experiment shown in panel B. Results represent the means and standard deviations of 10 mice per group. (C and D) Mice were passively immunized with 200 μg of murine IgG antibody to HSV-1 (murine immune globulin [MuIG]) or murine nonimmune IgG (NMuIG) and infected with 5 × 105 PFU of the rescue strain (C) or 5 × 105 PFU of NS-gE264 (D). Zosteriform disease scores in mice that received MuIG were significantly lower than the NMuIG-treated mice on days 5 to 7. Results are the means and standard deviations of 10 animals per group. (E and F) DRG titers in mice passively immunized with 200 μg NHuIG or HuIG and infected with 5 × 105 PFU of the rescue virus (E) or 5 × 105 PFU of NS-gE264 (F). No difference was detected between NHuIG and HuIG in (E), while a significant difference was detected on day 3 in the experiment shown in panel F. LOD, limit of detection of the assay, which is 2.5 PFU. Results are the means and standard deviations of five animals per group. (G and H) Mice were infected with 5 × 105 PFU of the rescue virus (G) or 5 × 105 PFU of NS-gE264 (H) and 56 h postinfection were passively immunized with 2 mg of NHuIG or HuIG. No difference was detected in zosteriform disease in animals infected with the rescue virus (G), while significant differences were noted in the NS-gE264 mice on days 6 and 7 postinfection (H). Results are the means and standard deviations of 10 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.