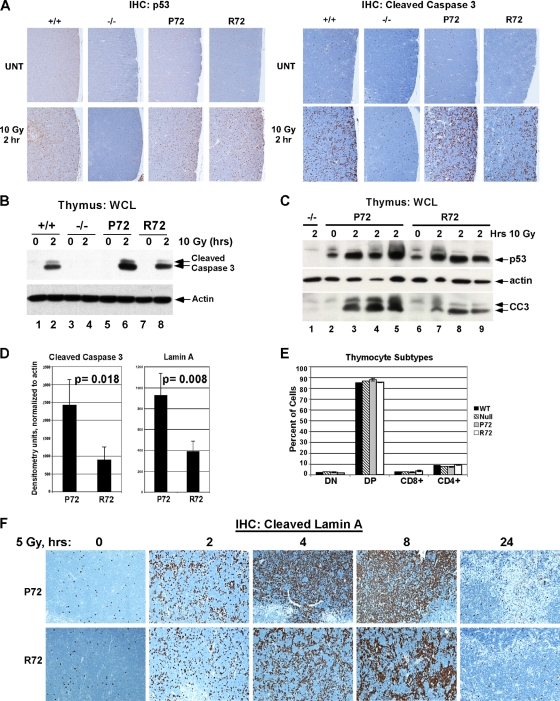
FIG. 2.
Increased apoptosis in P72 thymocytes following ionizing radiation. (A) Wild-type (+/+), p53-null (−/−), P72, and R72 mice were irradiated with 10 Gy, and after 2 h, thymuses were collected and subjected to immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of p53 (left) and cleaved (activated) caspase 3 (right). UNT, untreated. (B) Western analysis of thymic extracts from P72 and R72 mice and p53-null mice (−/−) that were irradiated with 10 Gy, harvested after 2 h, and probed for p53, actin, and cleaved caspase 3 (CC3). The lower-molecular-weight band is the fully active form of caspase 3. WCL, whole-cell lysate. (C) As in panel B, except that sibling littermates were analyzed. (D) The averaged densitometry results for Western analyses for cleaved caspase 3 shown in panel B and cleaved lamin A in irradiated thymocytes normalized to actin. The data depicted are averaged values from 3 mice per genotype. Statistical significance was calculated using the Student's t test. (E) Thymocytes were isolated from P72, R72, wild-type, and p53-null mice and subjected to fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis of the cell surface markers CD8 and CD4. The percentages of cells that were double negative (DN), double positive (DP), or singly positive (CD8+ and CD4+) were graphed. Three mice with each genotype were analyzed. (F) Immunohistochemical analysis of cleaved lamin A obtained from thymuses from P72 and R72 mice that were irradiated with 5 Gy and harvested after the times indicated.