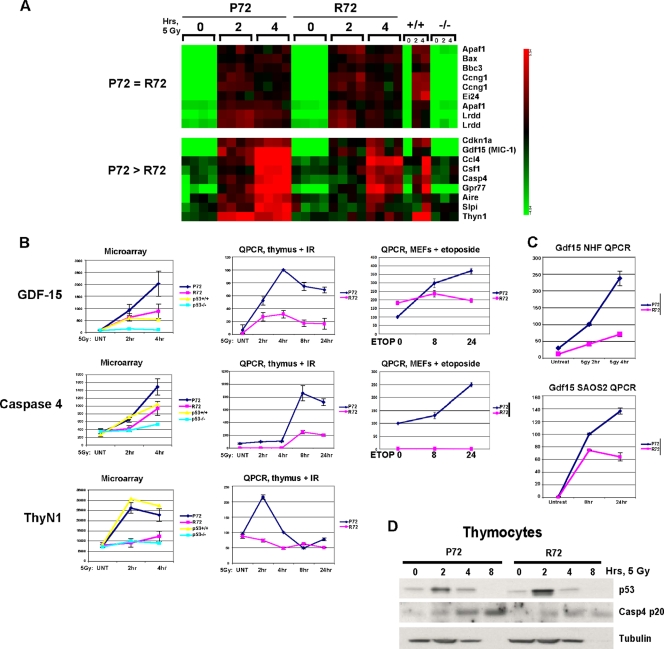
FIG. 3.
Increased expression of Gdf15, Casp4, and ThyN1 in the P72 thymus after irradiation. (A) Portions of the heat map generated from microarray analysis of thymocytes purified from P72, R72, wild-type (+/+), and p53-null (−/−) mice following treatment with 5 Gy and harvested after 2 or 4 h. Each square represents one of four independent biological replicates, using 2 mice per genotype. (B, left) Graphic representation of the generated microarray data shown in panel A, showing values for Gdf-15, caspase 4/11, and ThyN1. (Middle) QPCR analysis of a time course experiment with an independent set of thymocyte RNA samples for P72 and R72 thymocytes following treatment with 5 Gy, depicting Gdf-15, caspase 4/11, and ThyN1. IR, ionizing radiation. (Right) QPCR of RNA isolated from P72 and R72 mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) treated with 100 μM etoposide for 0, 8, or 24 h. The results depicted are averaged values from four independent QPCR samples performed in duplicate; the error bars depict standard errors. (C, top) QPCR of the Gdf15 level in normal human fibroblasts (NHFs) homozygous for either P72 or R72 that were irradiated with 5 Gy and harvested after 2 and 4 h. (Bottom) QPCR of the Gdf15 level in Saos-2 cells containing a temperature-sensitive inducible form of P72 or R72 shifted to the permissive temperature (wild-type p53) for 8 and 24 h. (D) Western analysis of thymocytes purified from P72 and R72 mice following irradiation with 5 Gy and harvested after the time points indicated for p53, caspase 4/11 (Casp4 p20), and tubulin; the loss of tubulin at 8 h likely represents substantial cell death at this time point.