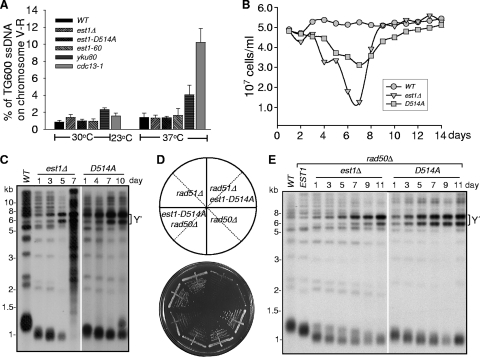
FIG. 5.
Y′ amplification takes place in the est1-D514A mutant to repair deprotected telomeres. (A) QAOS analysis of the est1 mutant as described in the legend to Fig. 2B. est1Δ, est1-D514A, and est1-60 haploid strains were generated from tetrad dissection. Wild-type and yku80Δ cells cultured at 30 or 37°C or the cdc13-1 mutant cells cultured at 23 or 37°C were used as negative or positive controls. (B) Cell viability assay for the est1 mutants. Dissected est1Δ spores carrying empty vector, pRS316-EST1, or pRS316-est1-D514A plasmid were grown in selective medium until the culture reached growth saturation, and each culture was diluted to an OD600 of ∼0.05 every day (24 h) for 14 days. The total cell number was determined after each indicated day. (C) Analysis of the telomere length of the est1 mutant strains. Genomic DNA was isolated from the yeast cells in panel B, digested with XhoI, and subjected to Southern blot analysis with a TG probe. The numbers at the top indicate the number of days the cells were grown. (D) Growth analysis of rad50Δ est1-D514A and rad51Δ est1-D514A mutants. est1Δ rad50Δ or est1Δ rad51Δ cells carrying either the pRS316-EST1 or the pRS316-est1-D514A mutant plasmid were grown repeatedly in Ura− medium until survivors were generated, and the 6th restreak is shown. (E) Telomere Southern blot analysis of rad50Δ est1-D514A and rad50Δ est1Δ mutant strains. Genomic DNA isolated from the indicated isogenic strains was digested with XhoI and subjected to Southern blot analysis using a TG probe. The numbers at the top indicate the numbers of days the cells were passaged.