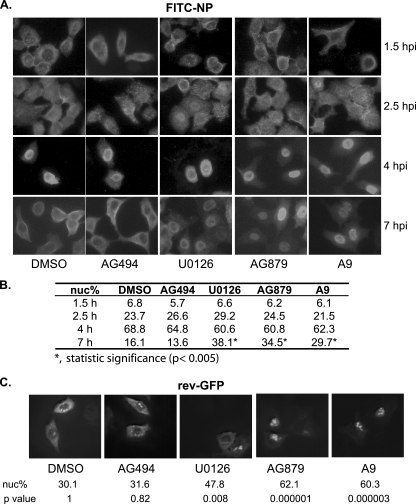
FIG. 4.
RTKIs AG879 and A9 impair the nuclear export of influenza vRNPs by inhibiting the host Crm1-dependent pathway. (A) A549 cells were infected with A/WSN virus and treated with either DMSO vehicle control or chemical inhibitors. At various time points, cells were stained with anti-NP antibody, followed by FITC-conjugated secondary antibody, and observed under a fluorescence microscope. A representative image from each condition is shown. Three independent experiments were conducted. (B) Quantification of the percentage of NP-FITC nuclear signal (nuc%). Results shown are the average from 40 cells for each drug treatment at each time point. Statistical analysis was conducted as described in Materials and Methods, and statistical significance as determined by t test is shown. (C) A549 cells were transfected with the rev-GFP fusion protein expression vector and treated with DMSO or respective inhibitors for 4 h prior to observation under a fluorescence microscope. For each treatment, the average percentage of rev-GFP nuclear signal (nuc%) and the P value of pairwise statistical comparisons to the DMSO control group are shown.