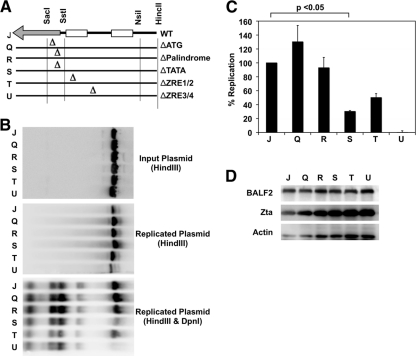
FIG. 2.
BHLF1 RNA is required for OriLyt function in cis. (A) Insertional mutations were made to disrupt several regions of the OriLyt sequence cloned into the pBluescript vector. These mutant plasmids were then tested for their ability to support lytic replication. (B) Wild-type or mutant pBluescript-OriLyt or vector control plasmids were transected into ZKO-293 cells along with the BZLF1 gene. Plasmids were analyzed by Southern blotting before (top panel) or after (center and bottom panels) transfection and lytic induction. Plasmids recovered from cells were digested with or without DpnI enzyme (as indicated). One representative experiment is shown. (C) Relative plasmid amounts were quantified using quantitative Southern blotting. Results were calculated as the DpnI-digested signal divided by the input plasmid signal and normalized to the value obtained for wild-type OriLyt. Data averages from three independent experiments are shown, with error bars representing the standard deviations. Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed, unpaired t test. (D) Western blot assays were used to monitor Zta and BALF2 protein expression levels in all transfected cells.