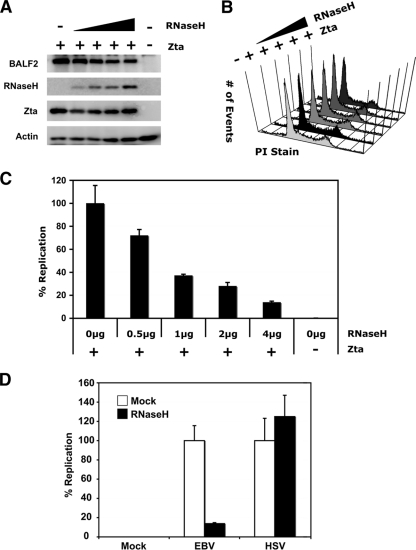
FIG. 7.
RNase H1 impairs EBV lytic replication. ZKO-293 cells were cotransfected with or without BZLF1 and RNase H1 expression plasmids or control vectors as shown. (A) Western blot assays were used to monitor Zta, RNase H1, and BALF2 protein expression levels in all transfected cells. (B) After 48 h, cells were analyzed for potential changes in viability and cell cycle. (C) At the same time, viral DNA was isolated and analyzed by real-time qPCR. Results were calculated as the signal obtained using EBV genome-specific (BNRF1) primers over the signal obtained using primers for cellular DNA (GAPDH) and normalized to the positive control expressing BZLF1 only. (D) 293 cells were transfected with RNase H1 (black bars) or vector control plasmids (white bars) and infected with HSV1 (as indicated) or mock infected 24 h posttransfection. At 10 h postinfection, cell were lysed and RNase H1 expression was confirmed by Western blotting (data not shown). DNA was isolated from cell lysates and analyzed by real-time qPCR. Results were calculated as the signal obtained using viral genome-specific (TKp) primers over the signal obtained using primers for cellular DNA (GAPDH) and normalized to the positive-control sample, which was infected with virus but not transfected with RNase H1.