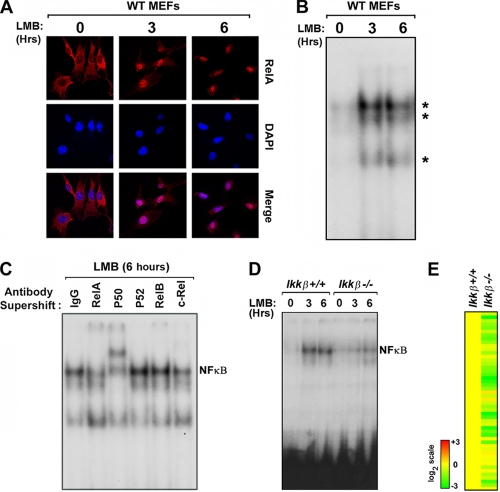
FIG. 4.
RelA shuttles through the nucleus of unstimulated cells to control autocrine IFN-β via IKK-β. (A) Wild-type MEFs were treated with the nuclear export inhibitor leptomycin B (LMB, 20nM) for 3 or 6 h and stained with antibodies to RelA. Cells were subsequently examined for RelA localization by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Nuclei were detected with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). (B) Nuclear extracts from wild-type MEFs treated with LMB for 3 or 6 h were subjected to EMSA using a radiolabeled PRD II probe. (C) Nuclear extracts from wild-type MEFs treated with LMB for 6 h were preincubated with the indicated anti-NF-κB subunit antibodies. Supershift of NF-κB complexes was examined by EMSA. (D) Nuclear extracts from ikkβ+/+ and ikkβ−/− MEFs treated with LMB for three or 6 h were subjected to EMSA using a radiolabeled PRD II probe. Note that all LMB experiments were performed in serum-free medium to exclude nonspecific NF-κB activation by serum components. Experiments whose results are shown in panels A to D were repeated at least three times with similar results. (E) Basal expression of the autocrine IFN-β signature was evaluated in unstimulated ikkβ+/+ and and ikkβ−/− MEFs. Basal expression of the autocrine IFN-β signature in ikkβ+/+ MEFs was normalized to one (20; yellow). The heat bar on the left represents relative expression levels on a log2 scale.