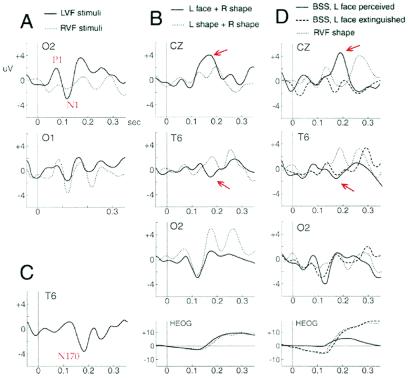
Figure 4.
ERPs at right occipital (O2), left occipital (O1), right posterior temporal (T6), and midline electrodes (CZ) for different conditions during 300-ms poststimulus onset. (A) Unilateral stimuli (faces and shapes) in RVF and LVF evoked an early contralateral occipital positivity at ≈80 ms (P1) and negativity at ≈120 ms (N1). (B) Lfs in bilateral trials (BSSfs) as opposed to Lss (BSSss) evoked a specific negativity at right posterior temporal site (≈170 ms postonset) and a positivity at midline (≈190 ms postonset), but similar occipital N1 (regardless of perception, as in averaged ERPs shown here). Eye movements (HEOG) were similar and cannot explain this ERP difference. (C) Difference waveform obtained by subtracting ERPs to Lfs from ERPs to Lss in BSS, clearly showing a face-specific negativity in right temporal region (N170). (D) Perception versus extinction. Compared with a Rs alone (Rs), bilateral stimuli with a LVF face (BSSfs) evoked a right occipital N1 and a temporal N170, both when the face was seen and when it was extinguished. Eye movements were similar during Rs and extinction trials and cannot explain this ERP difference. A later positivity at midline (≈190 ms postonset) occurred only when faces were seen (P190). Oculographic differences after ≈200 ms might partly contribute to this signal.