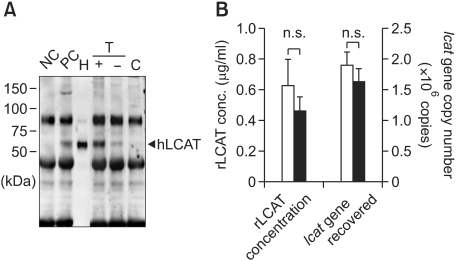
Figure 2.
Detection of hLCAT and survival of human lcat gene after transplantation of lcat gene-expressing m-ccdPA. Human lcat gene-transduced mouse ccdPA (5 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously transplanted in nude mouse with fibrin glue as a scaffold. (A) Existence of hLCAT protein in mice sera was detected by IP-Western experiments. 15 µg human high density lipoprotein (HDL) was loaded for quantification of signals (H). Mouse serum with (PC) or without (NC) 15 µg HDL were subjected to IP-Western. The gene-transduced (T) m-ccdPA were transplanted with (+) or without (-) fibrin glue. Sera (100 µl) from the mice and mice transplanted with un-transduced (C) m-ccdPA were subjected to IP-Western analysis. (B) Human lcat gene-transduced mouse ccdPA (5 × 106 cells) were transplanted after three days of culture with (open bars) or without (closed bars) adipogenic differentiation medium. The serum concentrations of the hlcat protein were quantified by densitometric analysis (left), and the human lcat gene was quantified in excised implants (right).