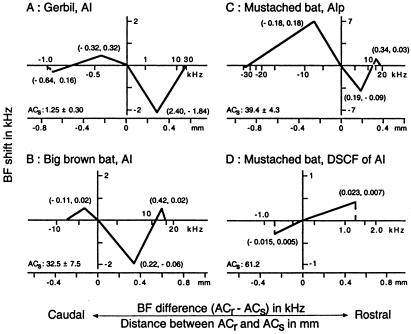
Figure 6.
Difference in BF shift among different mammalian species and between different cortical areas of a single species. BF shifts of cortical neurons along the frequency axis (ordinates) are plotted as a function of difference in BF (kHz) or distance (mm) between ACr and ACs. (A) AI of the Mongolian gerbil. (B) AI of the big brown bat (based on ref. 5). (C) AIp of the mustached bat. (D) DSCF area of the mustached bat (based on ref. 11). A pair of numbers in parentheses indicates a BF difference and BF shift in octave referring to the mean BF of ACs. Focal electric stimulation of cortical auditory neurons evokes BF shifts of adjacent cortical neurons toward (centripetal shift; A, B, and C) or away from (centrifugal shift; D) the BF of ACs. See the text.