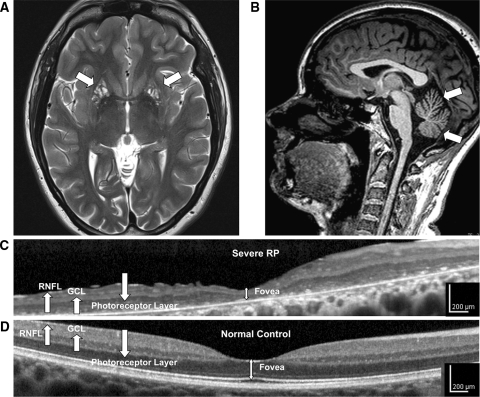
Fig. 1.
High-resolution retinal and brain imaging in NARP syndrome demonstrates analogous patterns of tissue injury. This 28-year-old woman (D1) with NARP syndrome from the mtDNA ATPase 6 m.8993T>C mutation with 78% blood leukocyte and 99% hair-bulb heteroplasmy had severe RP and moderate ataxia. a, b 3-T MRI demonstrates cystic and cavitary T2 hyperintensities in the bilateral putamina (a), likely reflecting neuronal necrosis, and also moderate cerebellar atrophy with T1 imaging (b). c High-resolution OCT image of the macula demonstrates severe retinal thinning, primarily due to degeneration of the photoreceptor and the retinal pigment epithelial cell layers, but also associated thinning of the ganglion cell (GCL) and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). d Macular OCT image from an age-similar normal female shown for comparison