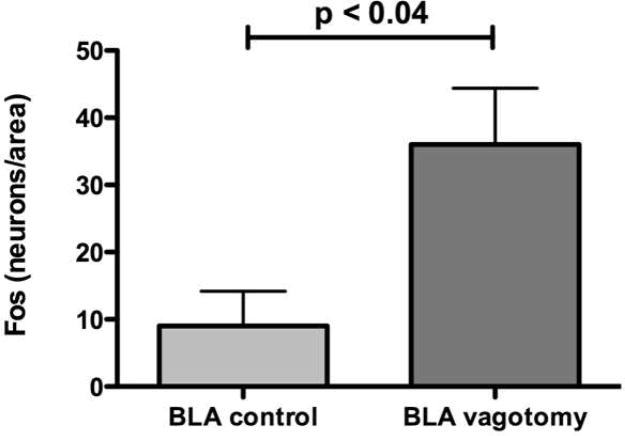
Figure 6.
Animals were subjected to 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis and to vagotomy (n = 4) or sham (n = 4) operation. Fos immunoreactivity was again demonstrated and the numbers of neurons/unit area was determined at multiple levels. Except in the anterior basolateral amygdala (BLA), no significant differences were found in the brain regions that were examined. Unlike the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH), central amygdala (CeA), and piriform cortex (PIR), the density (number/unit area) of Fos-ir neurons at this level of the basolateral amygdala (BLA) was significantly increased, not decreased by subdiaphragmatic vagotomy, suggesting that tonic vagal inhibition of the activity of neurons occurs in the BLA.