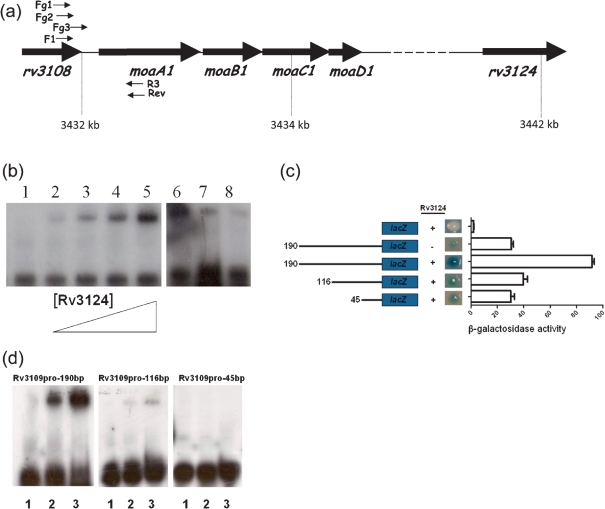
Fig. 3.
Binding of Rv3124 to the rv3108–moa1A intergenic region. (a) The moaA1 locus showing locus organization and positions of oligonucleotides used in EMSA and lacZ fusions. Primers F1 and R3 were used to generate the Rv3109pro product used in EMSA assays; primers Fg1, Fg2, Fg3 and Rev were used to generate products for lacZ-transcriptional fusions. (b) EMSA was performed in the absence of Rv3124 (lane 1) or in the presence of 0.15, 0.3, 0.6 or 1.2 μg purified Rv3124 (lanes 2–5). Competition was performed with Rv3124 (2.4 μg) with no competitor (lane 6) or with unlabelled specific competitor rv3109 probe (10-fold and 100-fold molar excess, lane 7 and lane 8, respectively). (c) β-Galactosidase activity of promoter-probe constructs in wild-type M. smegmatis mc2155 (denoted by ‘−’) and M. smegmatis overexpressing Rv3124 (denoted by ‘+’). Activity was monitored by plating strains on medium containing X-Gal and by quantitative β-galactosidase assay. Data are shown as Miller units, and are the mean±sd of three replicates. (d) Binding assay with full-length and truncated versions of the Rv3109pro probe (190 bp, 116 bp and 45 bp) in the absence of Rv3124 (lane 1) or in the presence of 0.6 μg and 1.2 μg Rv3124 (lanes 2 and 3 respectively). Decreased Rv3124 binding to the shorter probes correlates with reduced β-galactosidase activity in the corresponding lacZ transcriptional fusions.