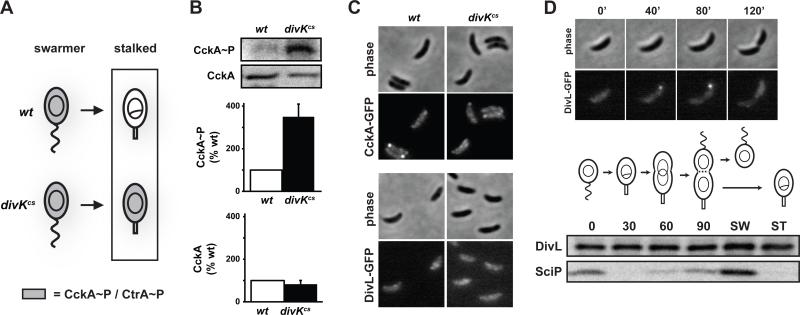
Figure 3. DivK inhibits CckA kinase activity at the G1-S transition.
(A) Diagram of CckA and CtrA activity during the swarmer-to-stalked cell transition in wild type and divKcs. (B) In vivo phosphorylation measurements of CckA in synchronized stalked cells harboring either divK or divKcs at the native chromosomal locus. Assays were performed as in Fig. 2A, except that stalked cells were isolated by allowing synchronized swarmer cells to differentiate for 50 minutes at 20°C, the restrictive temperature for divKcs. Error bars represent standard deviations from three independent replicates. (C) Fluorescence microscopy of wild type and divKcs stalked cells expressing CckA-EGFP. Strains were grown and stalked cells isolated exactly as in panel B. (D) Cell cycle localization pattern of DivL-EGFP. Swarmer cells expressing divL-gfp were isolated, placed on agarose pads containing M2G+ and followed by time-lapse fluorescence microscopy (top). Cell cycle Western blot analysis of DivL and SciP (bottom). Swarmer cells were isolated, released into rich media with samples taken for Western blot analysis every 30 minutes. Samples were also taken from swarmer (SW) and stalked (ST) cells collected immediately after cell division.