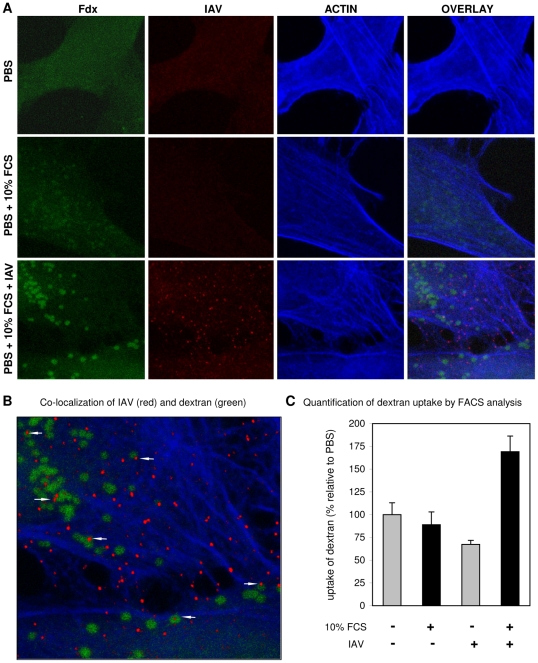
Figure 8. Induction of uptake of dextran into vesicles by the combined action of serum and IAV.
(A) Uptake of FITC-dextran (Fdx; green) into HeLa cells in PBS, PBS+10% serum or PBS+10% serum+IAV (MOI = 10) was studied by confocal microscopy. IAV was detected by fluorescence staining with monoclonal antibody directed against NP. The actin network of cells was stained by phalloidin. Whereas vesicular structures containing Fdx become visible in the presence of serum, these structures become much more apparent in the simultaneous presence of serum and IAV. (B) A magnification of Panel A demonstrating the co-localization of Fdx and IAV in vesicular structures (arrows). (C) Quantification of dextran uptake in presence or absence of IAV by FACS analysis. Fdx uptake was performed for 15 min at 37°C in PBS (grey bars) or in PBS containing 10% FCS (black bars) in absence or presence of IAV (strain WSN; MOI 10) as indicated at the x-axis. Background fluorescence from Fdx binding to the outside of cells was determined by performing the same experiment at 4°C (at which no endocytosis takes place) and was subtracted from the mean fluorescence intensity obtained at 37°C to determine the amount of fluorescent FITC-dextran that was internalized at 37°C. Data were plotted relative to FITC-dextran uptake in PBS in absence of IAV.