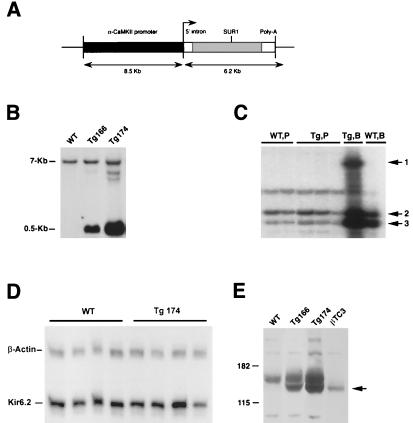
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the CMK-SUR1 construct for production of SUR1 Tg mice. (B) Genotyping of Tg mice by Southern blot. Mouse genomic DNA was extracted from mouse tail, digested with HindIII, and hybridized to a 5′ SUR1 probe. The 7-kb band corresponds to the endogenous mouse SUR1 gene and the 545-bp band corresponds to the transgene. (C) An RNase protection assay demonstrates expression of SUR1 transgene in brain (Tg,B, arrow 1), but not in pancreas (Tg,P, arrow 1). Expression of endogenous SUR1 (arrow 3) is roughly equivalent in pancreas (WT,P, n = 2; Tg,P, n = 3) and brain (WT,B, Tg,B, n = 1) from WT and Tg166 mice, relative to β-actin (arrow 2). (D) RNase protection assay shows no differences between WT (n = 4) and Tg174 (n = 4) mice in levels of expression of Kir6.2 message in forebrain. (E) SUR1 protein expression in forebrain from WT and Tg174 and Tg166 lines of mice indicated by immunoblot. The positive control consists of 30 μg of protein from a mouse pancreatic β-cell line (βTC3). The arrow points to multiple bands at ≈140 and 150 kDa, consistent with multiple glycosylation states of the SUR1.