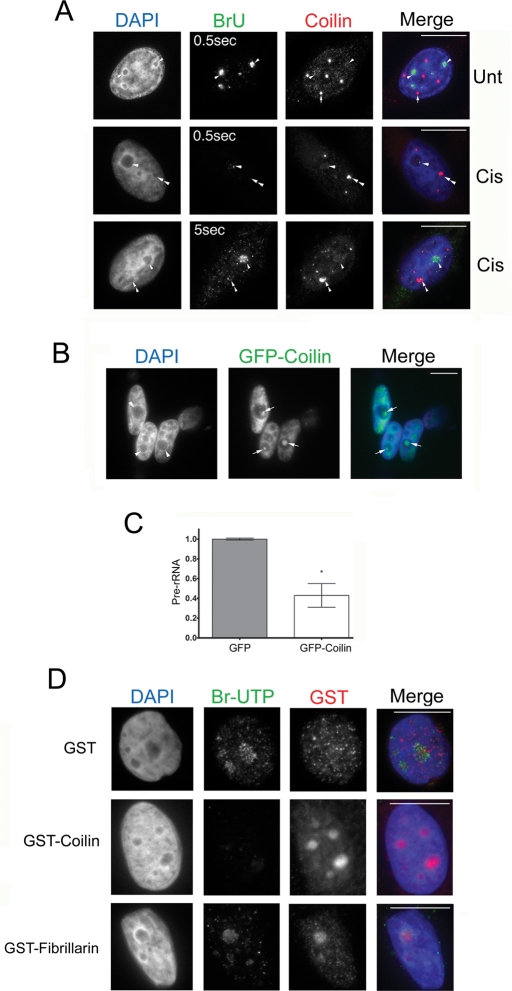
FIGURE 3:
Nucleolar coilin suppresses Pol I transcription. (A) Coilin-occupied nucleoli are associated with reduced BrU incorporation. Untreated or cisplatin-treated (24 h) HeLa cells were incubated in 2 mM BrU for 2 h followed by detection of Pol I transcripts with anti-BrdU antibodies (green) and coilin with anti-coilin antibodies (red) and DAPI staining (blue). Note that the BrU signal in the bottom panel was detected using a 5-s exposure. Arrowheads mark BrU-positive nucleoli, while arrows denote CBs. In treated cells, nucleoli with coilin accumulation (double arrowhead) lack BrU signal, yet BrU signal is present in nucleoli that lack intense coilin staining (arrowhead). Scale bars = 10 μm. (B) Transient expression of GFP-coilin results in nucleolar coilin. The nucleolar distribution of GFP-coilin (arrow) is typical of overexpressing cells, which represented ∼20% of transfected cells. Scale bars = 10 μm. (C) Transient expression of GFP-coilin reduces the level of pre-rRNA. RT-PCR was performed on RNA isolated from HeLa cells transfected with GFP-coilin or empty GFP vector. The amount of pre-rRNA was determined relative to GAPDH message levels. Data are normalized to the relative amount of pre-rRNA message obtained from HeLa cells transfected with empty GFP vector (error bars expressed as mean fold induction ± coefficient of variation [CV]; *p < 0.01) and reflect two independent experiments. (D) Exogenous coilin reduces BrUTP incorporation. In situ transcription run-on assay was performed on HeLa cells in the presence of bacterially purified GST-coilin, GST-fibrillarin, or GST. Cells were fixed and stained for BrUTP (green), GST (red), and DAPI (blue). Exposure times were the same for all images. Scale bars = 10 μm.