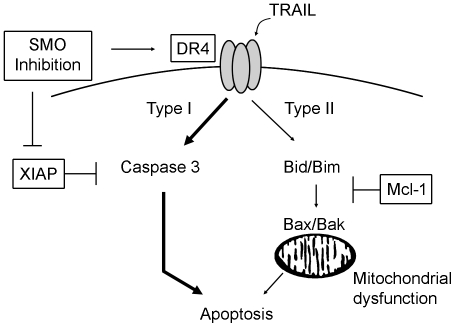
Figure 7. SMO inhibition sensitizes cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by increasing DR4 and decreasing XIAP protein levels, thereby switching cells from Type II to Type I death receptor signaling.
Schematic illustration of the interaction of Hedgehog and TRAIL signaling in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Death signaling upon TRAIL binding to DR4 normally is dependent on mitochondrial dysfunction (induced by Bid/Bim as well as Bak/Bax activation) to induce cholangiocarcinoma cell death (Type II pathway), a pathway blocked by elevated Mcl-1 protein levels in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Alternately, following DR4 ligation, robust caspase 3 activation can induce Type I death signaling, a pathway inhibited by XIAP expression under normal conditions. Inhibition of SMO expression or activity sensitizes cells to TRAIL via increasing DR4 [19] and decreasing XIAP levels, thereby switching cells from Type II to Type I death receptor signaling and promoting apoptosis.