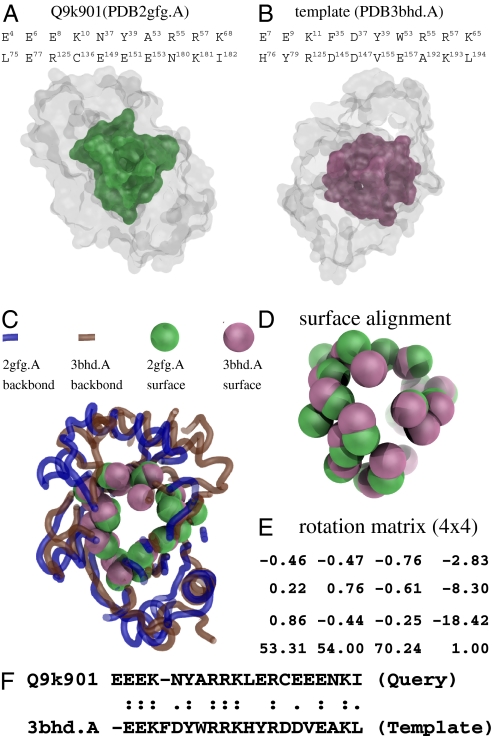
Fig. 5.
Shape analysis of the query structure (PDB2gfg.A) and the template (PDB3bhd.A). (A) The actual binding surface of the query. (B) The split pocket (actual binding surface) of the template. (C) The structural alignment is performed based on the superimposition of the two binding surfaces as shown in D by the specific rotation matrix in E, which was computed by the method of fPOP (7). The spatial matching has a RMSD of 2.6 Å at a significant P value of 6.93 × 10−7. (F) In terms of the binding site residues, the sequence identity of the two spatial patterns is as high as 50%, although the full-length sequences of the two proteins have a sequence identity of only ∼34%.