FIGURE 5.
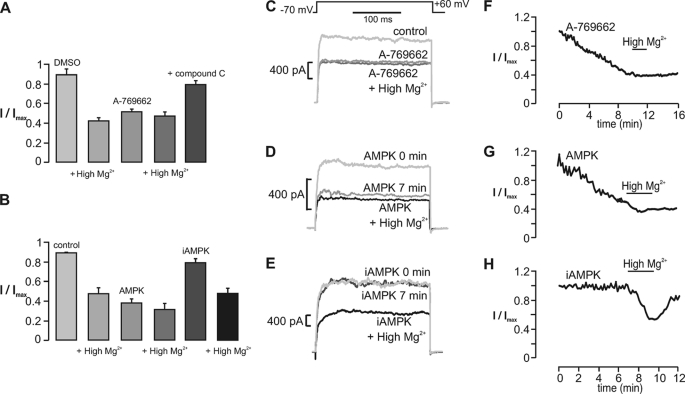
AMPK-dependent regulation of the large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ current in carotid body type I cells. A, bar chart shows the residual whole-cell K+ current (I/Imax; mean ± S.E. (error bars)) recorded under control (1:1000 DMSO) conditions and after a 15-min incubation with the AMPK agonist A-769662 (100 μm) both in the absence and presence of high Mg2+ and in the presence of A-769662 and compound C (40 μm). Upon switching to high Mg2+, residual outward current (I/Imax; mean ± S.E.) measured 0.48 ± 0.04 (p < 0.01; n = 7) from 0.92 ± 0.03. Residual current measured 0.53 ± 0.04 (p < 0.01; n = 7) after 10.28 ± 0.89 min with A-769662 (high Mg2+ = 0.43 ± 0.03; n = 6) and 0.81 ± 0.04 (n = 7) with A-769662 and compound C. B, bar chart shows the residual whole-cell K+ current (I/Imax; mean ± S.E.) recorded under control conditions and 13 min after intracellular dialysis of a constitutively active AMPK heterotrimer (AMPK; bacterially derived and thiophosphorylated α2β2γ1) or inactive AMPK heterotrimer (iAMPK; bacterially derived kinase-dead α2β2γ1) both in the absence and presence of high Mg2+. Residual current measured 0.37 ± 0.04 (p < 0.01; n = 6) after 7.53 ± 0.54 min with AMPK (high Mg2+ = 0.31 ± 0.05; p < 0.01; n = 6) and 0.79 ± 0.04 (n = 6) after 10 min with iAMPK (high Mg2+ = 0.48 ± 0.04; p < 0.01; n = 6). The middle panels show example records of whole-cell K+ current recorded before and after equilibration with A-769662 (C), AMPK (D), and iAMPK (E). The right-hand panels show the time course for inhibition of whole-cell K+ current during extracellular application of A-769662 (F) and intracellular dialysis of AMPK (G) and iAMPK (H).