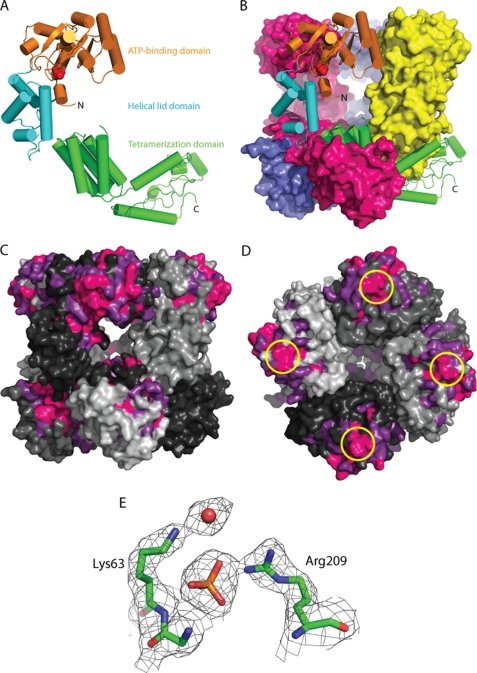
FIGURE 1.
Structure of the E. coli MgsA protein. A, ribbon diagram of a single MgsA protomer with ATP-binding domain (orange), lid domain (cyan), and tetramerization domain (green) colored to reflect the domain architecture. Phosphate is modeled in red. B, crystallographic asymmetric unit is shown with one protomer in ribbon form and the three remaining protomers in surface form. C, conservation of sequences in 157 MgsA homologs. Invariant (pink) and highly conserved (magenta) residues are color-coded. The four MgsA protomers of the asymmetric (and biological) unit are shown in four shades of gray. Areas of high conservation are apparent in the active site pocket and as the interface between subunits in the oligomerization domains. D, conservation around the Arg finger (circled in yellow); view is looking down on ATP-binding domain. E, view of a portion of the 2Fo − Fc electron density map contoured to 1.5σ superimposed with the refined MgsA structure.