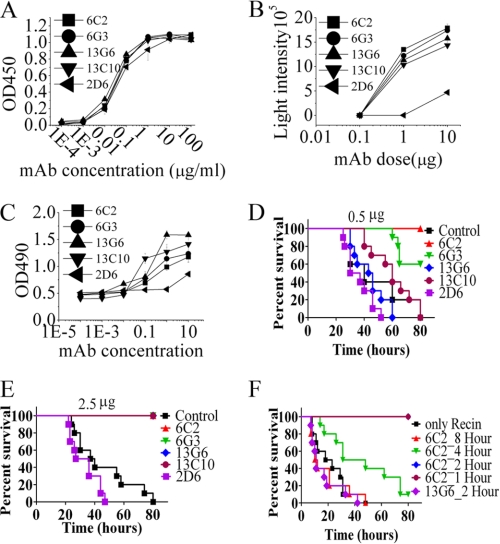
FIGURE 2.
Characterization and evaluation of mAbs against RTA. A, relative binding avidity of RTA mAbs. RTA mAbs were purified on protein G. Purified mAbs were titrated in ELISA for binding to RTA (100 ng/well). B, inhibition of ricin enzymatic activities by RTA mAbs. A fixed concentration of ricin holotoxin was mixed with varying concentrations of RTA mAb. The ability of mAbs to block the inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis was measured. C, Ab-mediated inhibition of ricin cytotoxicity. Vero cells were incubated with ricin (1 μg) and the indicated Ab. After 40 h, cell viability was assayed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide dye reduction. D–F, therapeutic efficacy of RTA mAbs. After an intraperitoneal injection of ricin into the left side on the basis of weight (50μ/kg), mice were administered a single dose of 0.5 μg (D) or 2.5 μg (E) of RTA mAb. Data reflect ∼10 mice per condition. F, efficacy of RTA-specific mAb therapy at different time points. A single dose (5 μg) of mAb 6C2 was administered either 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, or 8 h after the ricin injection. Data are mean ± S.D. of at least three experiments.