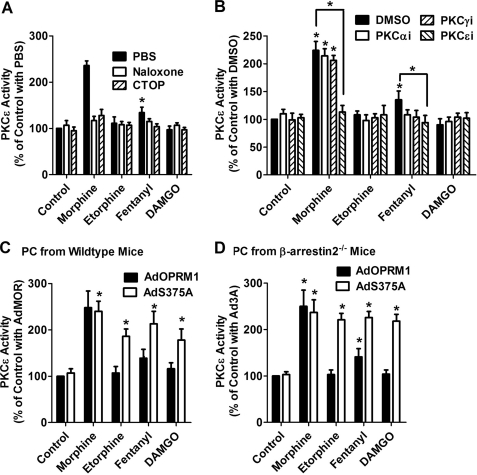
FIGURE 6.
Receptor phosphorylation attenuates PKCϵ activation in primary cultures. A and B, primary cultures of hippocampal neurons from wild-type mice were pretreated with PBS, 10 μm naloxone, or 10 μm CTOP for 10 min (A). The cultures were pretreated with DMSO or 50 μm PKC subtype-specific inhibitors (PKCαi, PKCγI, and PKCϵi) for 3 h (B). Then the primary cultures were incubated with 1 μm morphine, 10 nm etorphine, 10 nm fentanyl, or 1 μm DAMGO for 5 min, and the activities of PKC subtypes were determined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The results were normalized against that of the control with PBS (A) and the control with DMSO (B). C, primary hippocampal neurons from wild-type mice were infected with AdOPRM1 or AdS375A for 3 days. Then the primary cultures were incubated with 1 μm morphine, 10 nm etorphine, 10 nm fentanyl, or 1 μm DAMGO for 5 min, and the activity of PKCϵ was determined. The results were normalized against that of the control with AdOPRM1. D, primary hippocampal neurons from βarrestin2−/− mice were prepared as in C, and PKCϵ activity was determined.