Fig. 3.
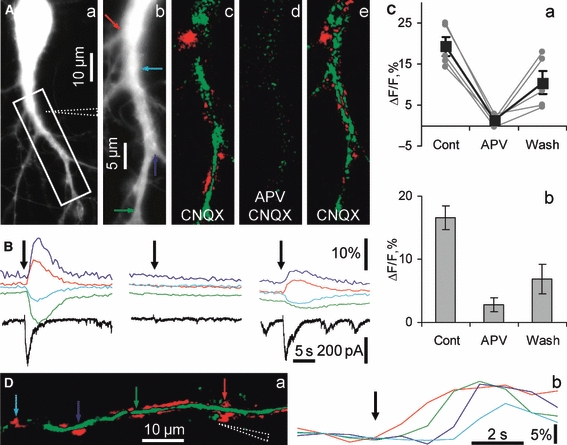
Hippocalcin-YFP translocated due to direct Ca2+influx via NMDARs. (A) Images demonstrating NMDAR-dependent hippocalcin-YFP translocation in a neuron stimulated by iontophoretically applied glutamate in Mg2+-free solution in the presence of CNQX (10 μm), gabazine (5 μm) and glycine (10 μm). A fluorescent image (a) was taken using the YFP filter set. The position of the iontophoretic pipette is indicated by dashed lines. (Ab) A higher magnification image of a dendritic branch shown in the boxed area in Aa. Differential pseudocolour images were taken at 2.5 s after an onset of iontophoretic glutamate application (0.5 s, 100 nA) in control (c) and APV-containing (d) solutions, and after APV washout (e). A green colour represents a decrease and red represents an increase in hippocalcin-YFP fluorescence. Colour arrows in b indicate sites where ROIs were placed. Time courses of fluorescence changes in these ROIs in control, APV (40 μm) and after blocker washout are shown in B. Colours of traces match arrow colours in Ab. Onsets of iontophoretic glutamate applications are shown by black arrows in B. The currents (black traces) were recorded in voltage clamp mode at -60 mV to abolish Ca2+influx via VOCC and leave NMDARs as the only source of Ca2+influx. (C) Representative (taken from five ‘red’ ROIs in the experiment shown in A) (a) and pooled (b) graphs showing strong suppression of hippocalcin-YFP translocation by APV. (D) Hippocalcin-YFP translocation due to local activation of NMDARs and site-specific association of hippocalcin-YFP with the plasma membrane. A diffusional wave of glutamate released from a pipette (shown by dashed lines in a) during an iontophoretic pulse (200 ms, 100 nA; onset of application is indicated by a black arrow in b) initially induced hippocalcin-YFP translocation in a dendritic branch in a site proximal to the pipette (red arrow), after that in a more distal site indicated by a green arrow and finally in the most distal sites (blue and cyan arrows). Colour coding of traces in (b) matches the colours of arrows in (a). The distance from the pipette tip to the most distal ROI is about 50 μm and the glutamate wave passed this distance for about 3 s, in agreement with an estimated rate of glutamate diffusion in the extracellular solution. There was no translocation in more distal dendritic sites, indicating that glutamate did not reach NMDARs in these sites.
