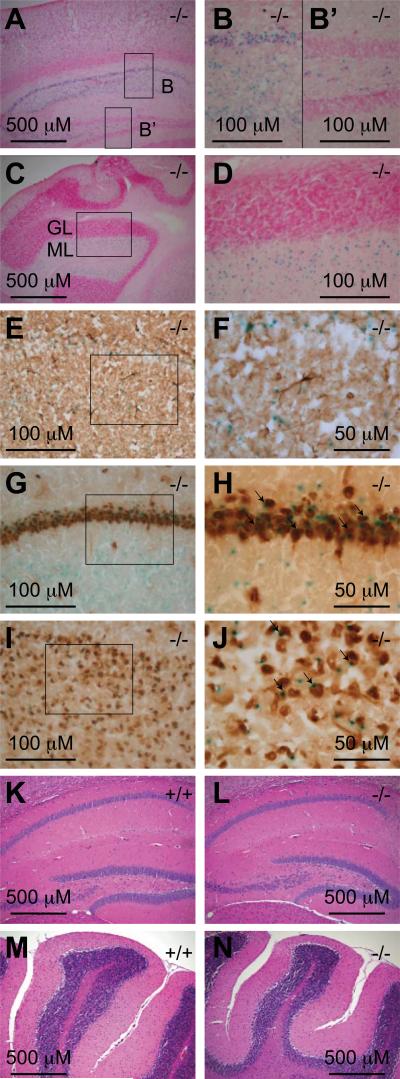
Fig. 7. Af17 is expressed in the neurons of adult animals.
A. X-gal staining of a sagittal brain section from an Af17-/- animal with stained cells in the cerebral cortex and the CA areas of the hippocampus. B & B’. High magnification images of the boxed areas in A. Note the staining in the CA areas but not in the dental gyrus. C. X-gal staining of a sagittal brain section from an Af17-/- mouse showing stained cells in the cerebellum. GL: granular layer; ML: molecular layer. D. A high magnification image of the boxed area in C. Sections in A-D were counterstained with nuclear fast red. E. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for GFAP in a transverse brain section after X-gal staining. Note that the blue X-gal staining and the brown IHC staining do not coexist in the same cells. F. A higher magnification image of the boxed area in E. G-J. IHC staining for NeuN and X-gal staining in a transverse brain section showing the hippocampal CA areas (G) and the cerebral cortex (I), with higher magnification images of their boxed areas shown in H and I, respectively. Note the cells stained by both X-gal and IHC (arrows). K-N. Hematoxylin & Eosin staining of sagittal brain sections from 6-8 week old WT (K & M) and Af17-/- (L & N) animals showing similar morphology of the hippocampus (K & L) and the cerebellum (M & N). All animals shown were 6 weeks old.