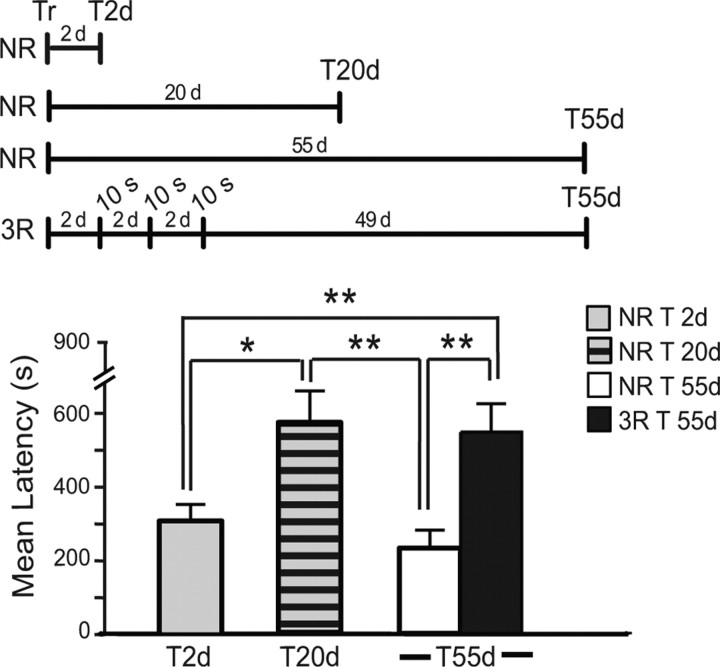
Figure 3.
Multiple reactivations make the memory resistant to forgetting. Experimental timelines are shown above the experiment. Animals were trained and divided in 4 groups: one group was tested 2 d after training (NR T2d), the second was tested 20 d after training (NR T20d); the third was tested 55 d after training (NR T55d). The last group underwent 3 × 10 s reactivations starting 2 d after training and with an interreactivation interval of 2 d, and was tested 55 d after training (3R T55d). NR T20d had a significantly stronger latency compared with NR T2d (*p < 0.05). The latency of NR T55d was significantly decreased compare with that of NR T20d (**p < 0.01). This decay of latency was completely rescued in 3R T55d (**p < 0.01).