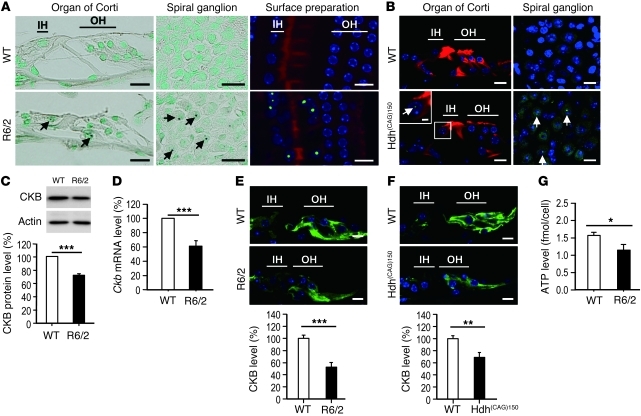
Figure 2. Auditory dysfunction in HD mice.
(A) Cochleae (mid-basal turn) of 10.5-week-old mice were visualized by immunohistochemistry (Htt, dark brown deposits; nuclei, green). NIIs (arrows) were detected in the spiral ganglion (middle panels) and in the organ of Corti (left panels) of R6/2 mice. Surface preparations (right panels; mid-basal turn) of 10.5-week-old mice were performed to detect NIIs using an anti-Htt antibody (green), nuclei using Hoechst 33258 (blue), and the organ of Corti using rhodamine phalloidin (red). IH, inner hair cell; OH, outer hair cell. (B) Cryosections of the cochlea of 15-month-old mice (mid-basal turn) were stained with an anti-ubiquitin antibody (green) and with rhodamine phalloidin (red). Arrows indicate NIIs. (C) Total protein (30 μg per lane) from the cochleae of 10.5-week-old WT and R6/2 mice was analyzed for the expression of CKB protein, which was normalized to that of actin. (D) RNA from cochleae of 10.5-week-old WT and R6/2 mice (n = 6 per group) was used to determine the level of the Ckb transcript using an RT-qPCR method. The expression levels of Ckb were normalized to those of a reference gene (Gapdh). (E) CKB immunostaining (green) of the cochlea of 12-week-old WT and R6/2 mice. (F) CKB immunostaining (green) of the cochleae of 20-month-old WT and Hdh(CAG)150 mice. Scale bars: 10 μm (A, B, E, and F) and 2 μm (inset in B). Quantitative analyses are shown in the lower panels (C, E, and F). (G) ATP level in isolated hair cells of 12-week-old WT and R6/2 mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.