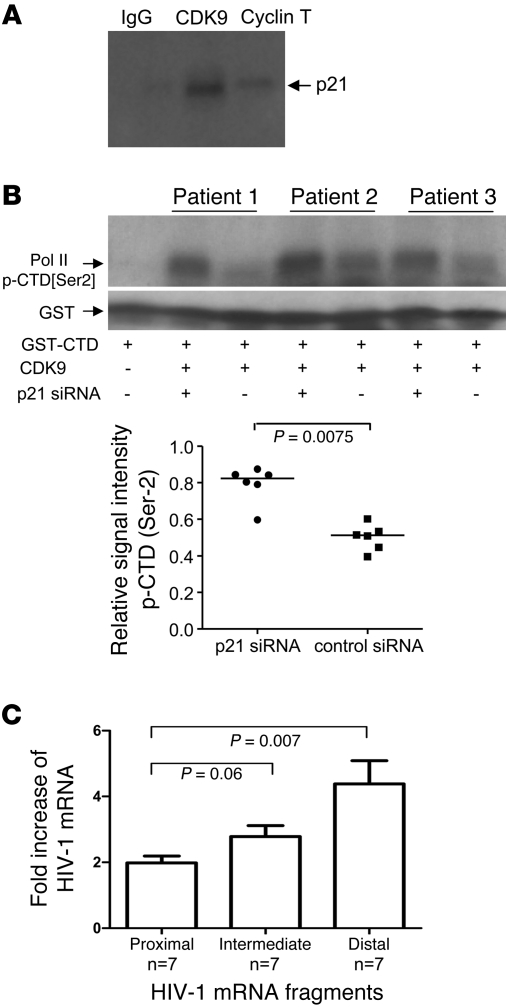
Figure 6. p21 inhibits enzymatic activity of CDK9 and affects HIV-1 transcriptional elongation.
(A) Whole protein lysates of CD4+ T cells from elite controllers were precipitated with anti-CDK9, anti–cyclin T, or unspecific anti-IgG control antibodies and subsequently interrogated with p21-specific antibodies using Western blotting. Shown is 1 representative experiment of 2. (B) Assessment of the enzymatic activity of CDK9 in CD4+ T cells from elite controllers electroporated with p21-specific or control siRNA. CDK9 isolated from electroporated CD4+ T cells was mixed with a recombinant, GST-tagged protein representing the CTD of human RNA polymerase II serving as a substrate for CDK9. Phosphorylation of CTD polymerase II was detected by phospho-Ser2–specific antibodies in 3 representative patients. Cumulative data from 6 patients per group are also shown. Statistical comparison was performed using paired Wilcoxon test. (C) Influence of p21 on transcription of proximal and distal HIV-1 mRNA transcripts. CD4+ T cells from elite controllers were infected with VSV-G–pseudotyped HIV-1 after treatment with p21 inhibitor or DMSO as control. Data are mean and SD fold increase in expression of proximal, intermediate, and distal HIV-1 mRNA transcripts in p21-deficient relative to control cells. Statistical comparison between expression intensity of different mRNA transcripts was performed using Mann-Whitney U test.