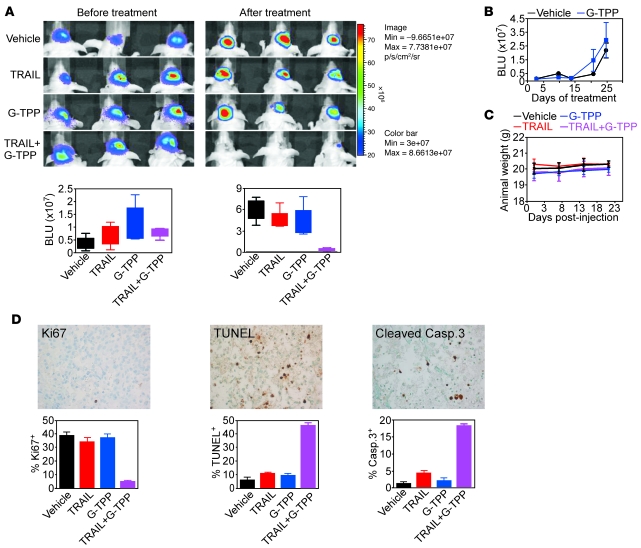
Figure 9. Exploitation of mitochondrial UPR for antiglioma therapy in vivo.
(A) Nude mice carrying intracranial U87-Luc glioblastomas were treated as indicated and analyzed by bioluminescence imaging (top). Bottom, quantification of bioluminescence signals before or after treatment. The statistical analysis of animal survival in the various groups at the end of the experiment is as follows: vehicle versus G-TPP, NS; vehicle versus TRAIL, NS; TRAIL (27 days) versus TRAIL+G-TPP (35 days), P = 0.0044; G-TPP (25 days) versus TRAIL+G-TPP (35 days), P = 0.0017; vehicle (24 days) versus TRAIL+G-TPP (35 days), P = 0.0014. (B) Nude mice carrying established intracranial glioblastomas as in A were treated with vehicle or G-TPP monotherapy at 20 mg/kg as daily i.p. injections and analyzed by bioluminescence imaging. Mean ± SEM of groups with mice as the individual units. P = 0.67. (C) Nude mice as in A were monitored for weight changes during the various treatments. Mean ± SD of individual groups. (D) Brain sections from TRAIL+G-TPP–treated mice were analyzed for cell proliferation (Ki67), internucleosomal DNA fragmentation (TUNEL), or active caspase-3 (top) by immunohistochemistry, and the percentage of positive cells was quantified (bottom). Original magnification, ×400.