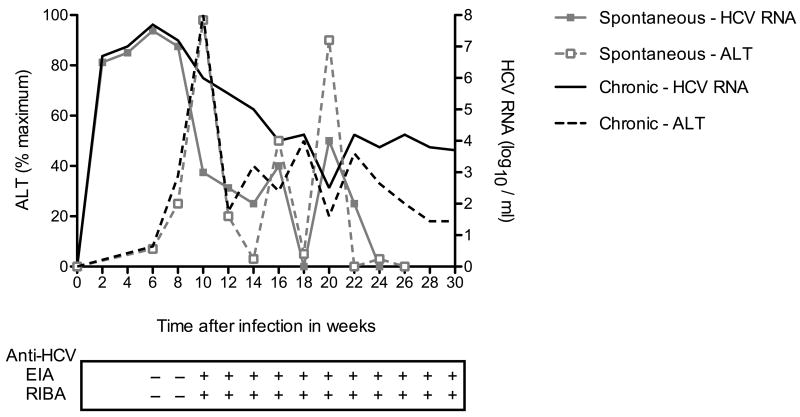
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of clinical and virological course of HCV in spontaneous resolvers versus chronically infected individuals. HCV RNA typically becomes detectable within 7-14 days after exposure and specific antibodies appear within 20 to 150 days, with a mean of approximately 60 days. Elevation of alanine aminotransferases (ALT) correlates with early immune responses and occurs after week 6, but may occur as early as the second week following exposure. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) detects antibodies to HCV. The recombinant immunoblot assay (RIBA) identifies the specific antigens to which antibodies are reacting in EIA.