Table 1.
Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators That Affect Cholangiocyte Proliferation and Function
| Neurotransmitter/neuromodulator | Structure | Receptors | Effect on proliferation/function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met-enkephalin | Delta, mu, and kappa ORs | Increase in opioid synthesis during cholestasis limits excessive cholangiocyte proliferation via delta OR | 13 | |
| Serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine | 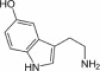 |
Serotonin 1A and 1B receptors | Autocrine loop based on serotonin secretion that limits the growth of the biliary tree during chronic cholestasis | 14 |
| Epinephrine/norepinephrine | 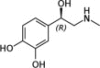 |
β1-ARβ2-AR | Required for cholangiocyte proliferation in response to BDL | 15–18 |
| α1-ARα2-AR | Regulation of secretin-stimulated ductal secretion | |||
| Acetylcholine | M3-ACh | Enhances the effect of secretin; required for cholangiocyte proliferation in response to BDL; maintains biliary mass | 19–22 | |
| GABA | GABAA, GABAB, GABAC receptors | After damage of large bile ducts by GABA, small ducts replenish the biliary tree by amplification of Ca2+-dependent signaling and de novo acquisition of large secretory phenotypes | 23 | |
| Anandamide | 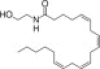 |
Cb1, VR1 | Anandamide inhibits cholangiocyte during BDL via activation of thioredoxin 1/redox factor 1 and AP-1 activation | 24 |
| Histamine | H1R, H3R | H3R agonist RAMH inhibits biliary growth of BDL rats; small mouse cholangiocytes proliferate in response to H1R stimulation | 25,26 |
AP-1, activator protein-1; AR, androgen receptor; OR, opiod receptor; RAMH, R-α-methylhistamine dihydrobromide.
